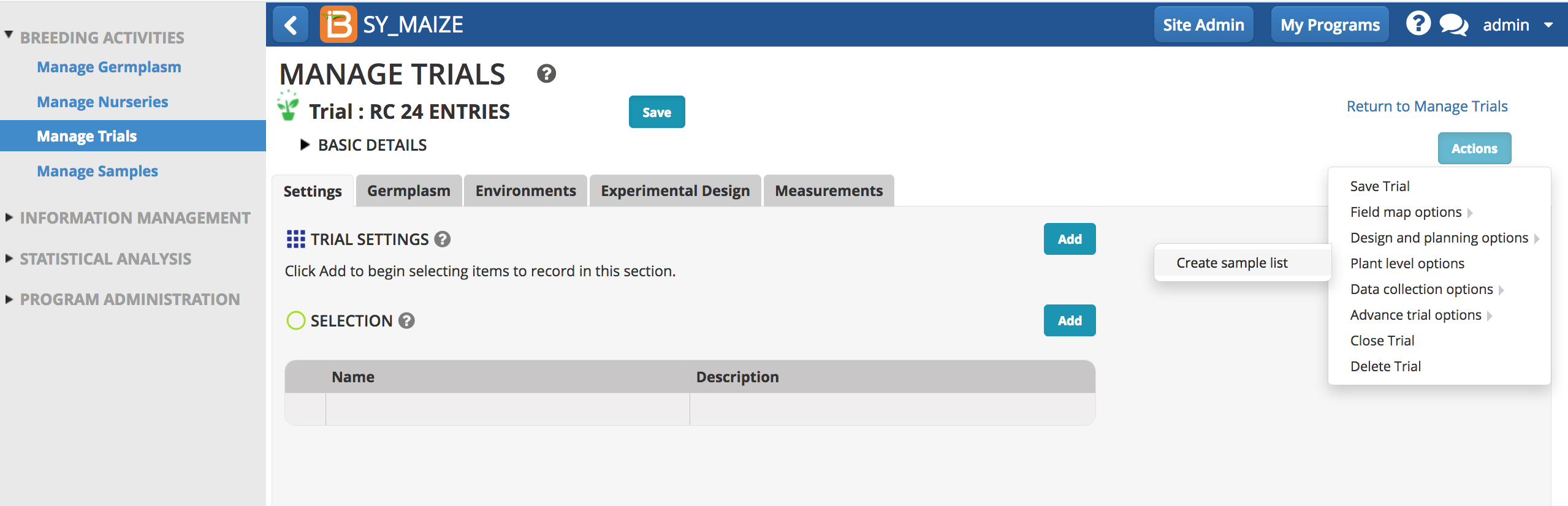
Start Trial
- Start a new trial or browse for existing trial.

Basic Details
Trial name and description are required before a trial can be saved.
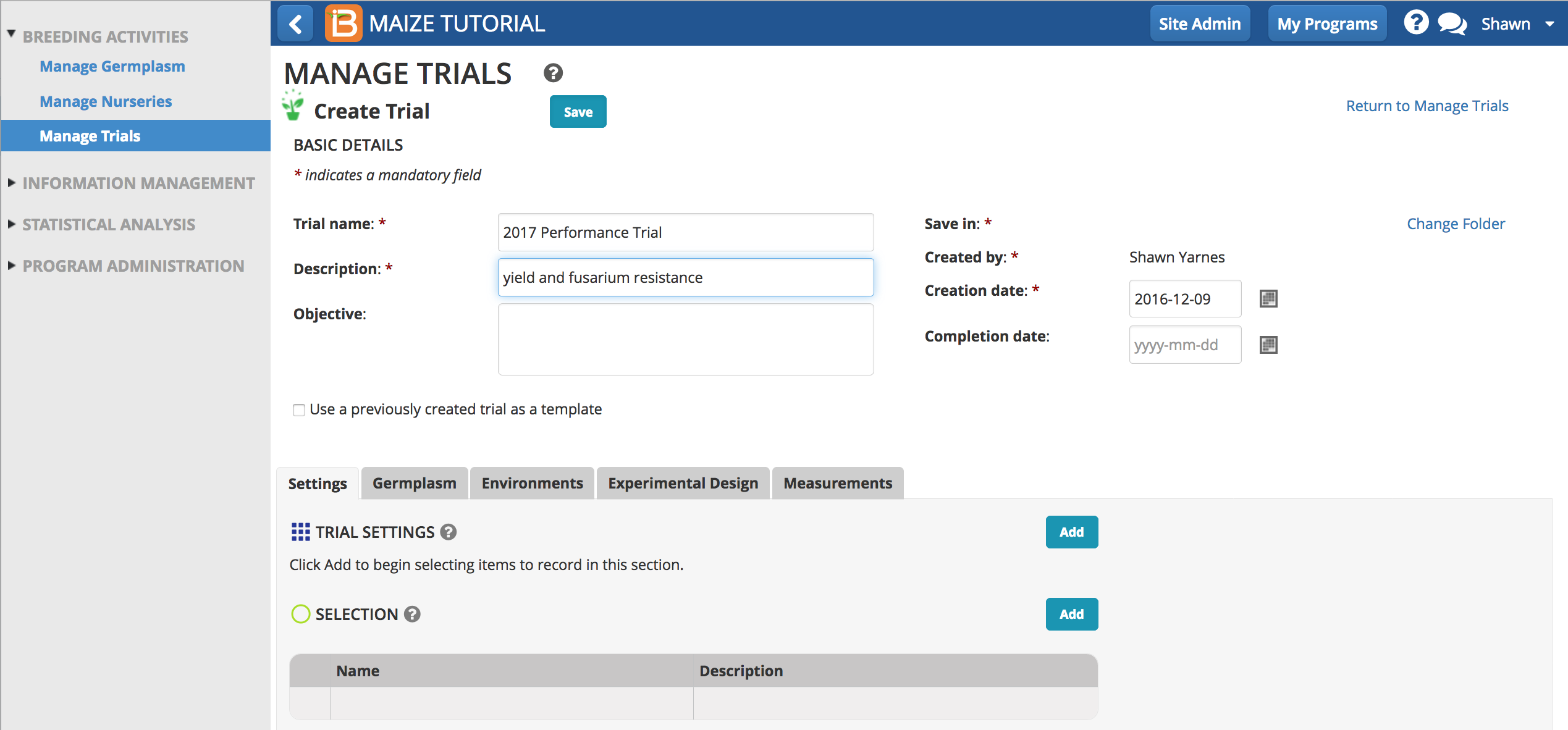
Save
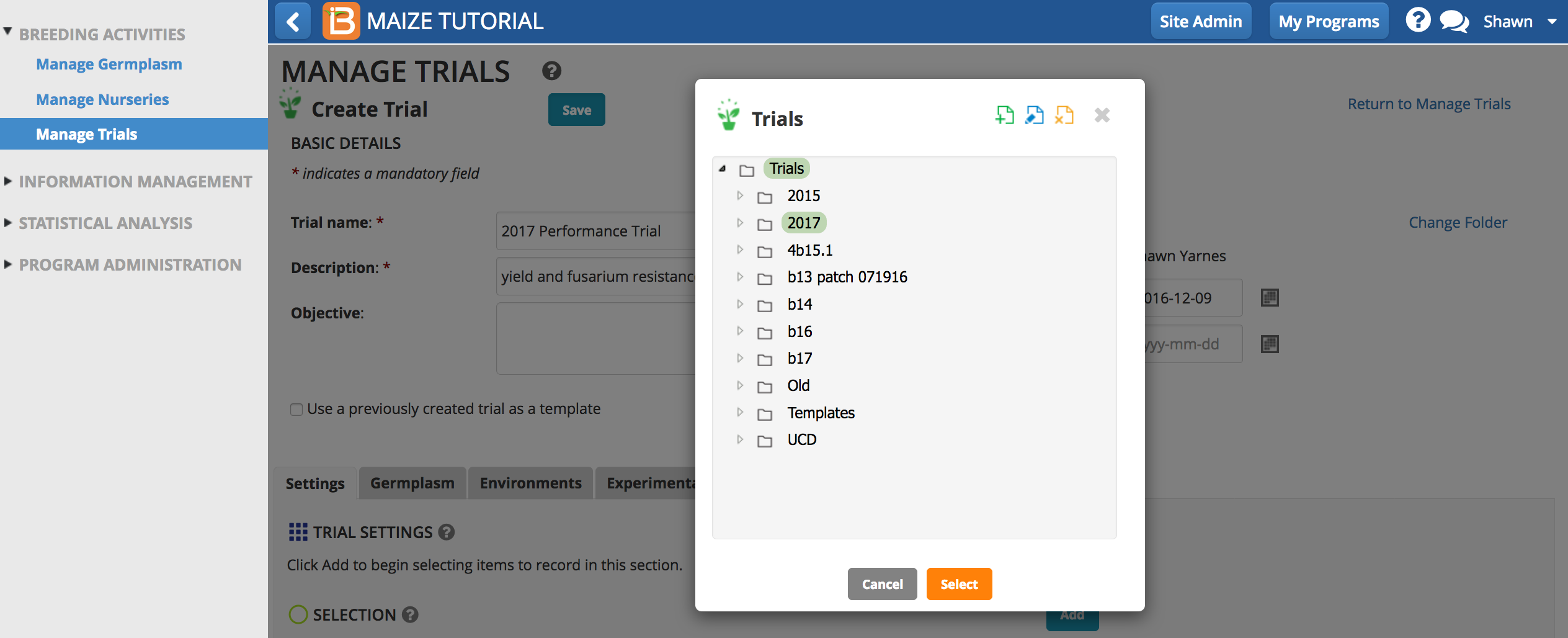
Select Save and specify the file directory where the trial will be stored in the database.
Template
Check the box to 'Use a previously created trial as a template'. Choose any previously created trial from the directory.
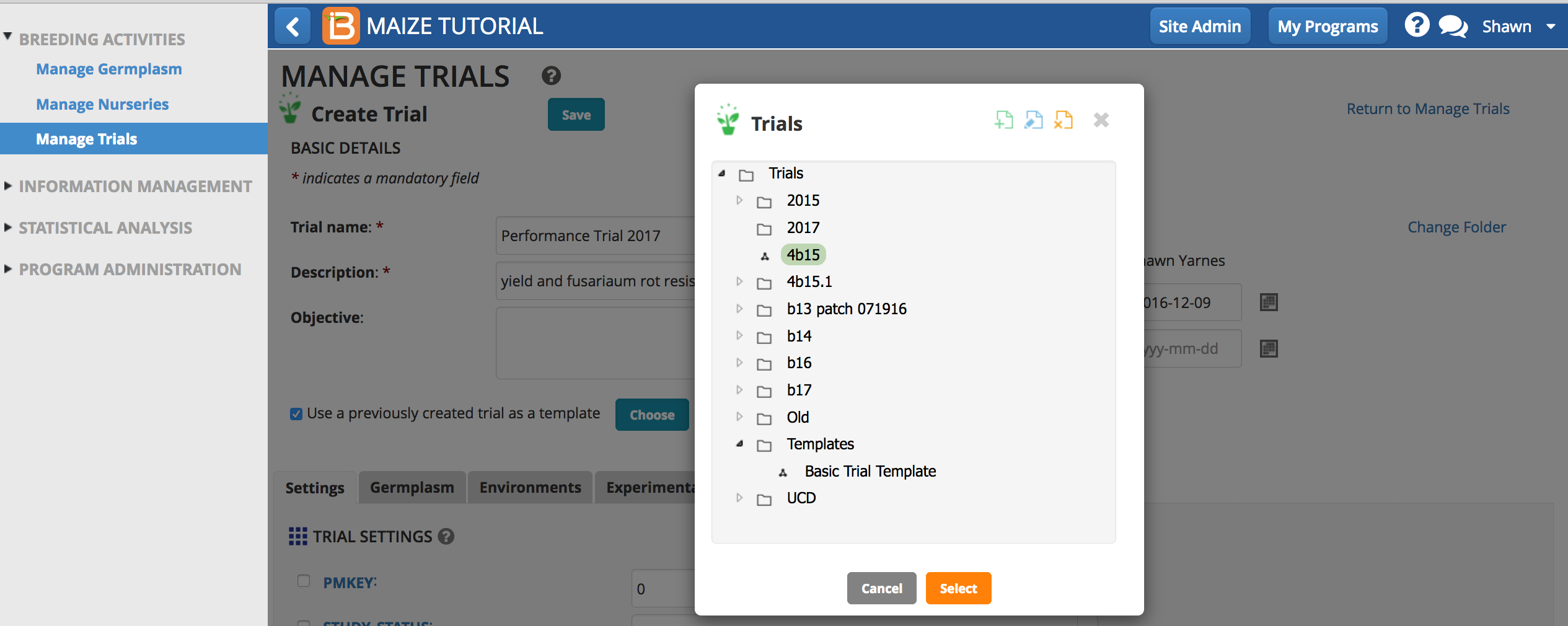
Once saved, Settings, Environments, and Traits from the previously created trial now populate the new trial.
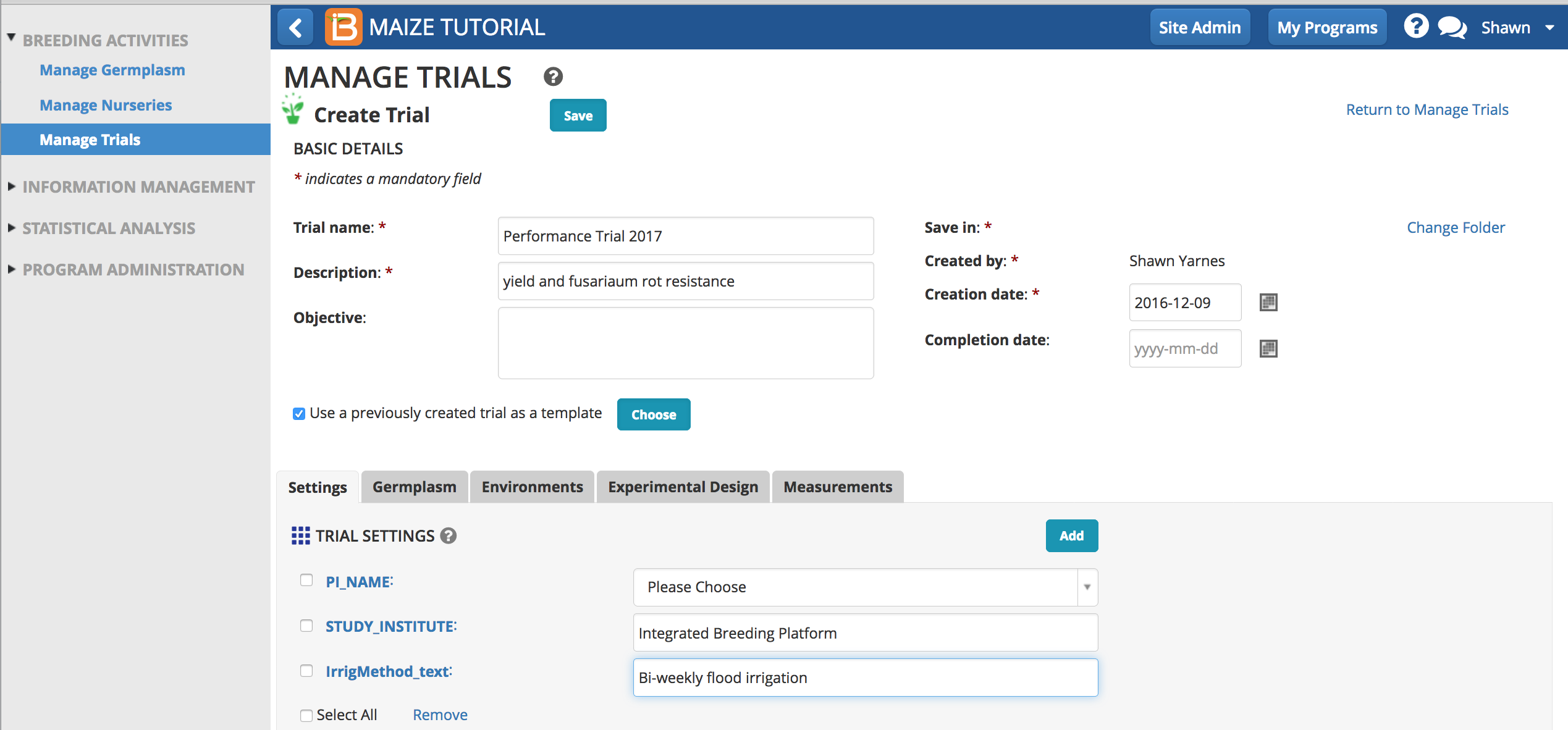
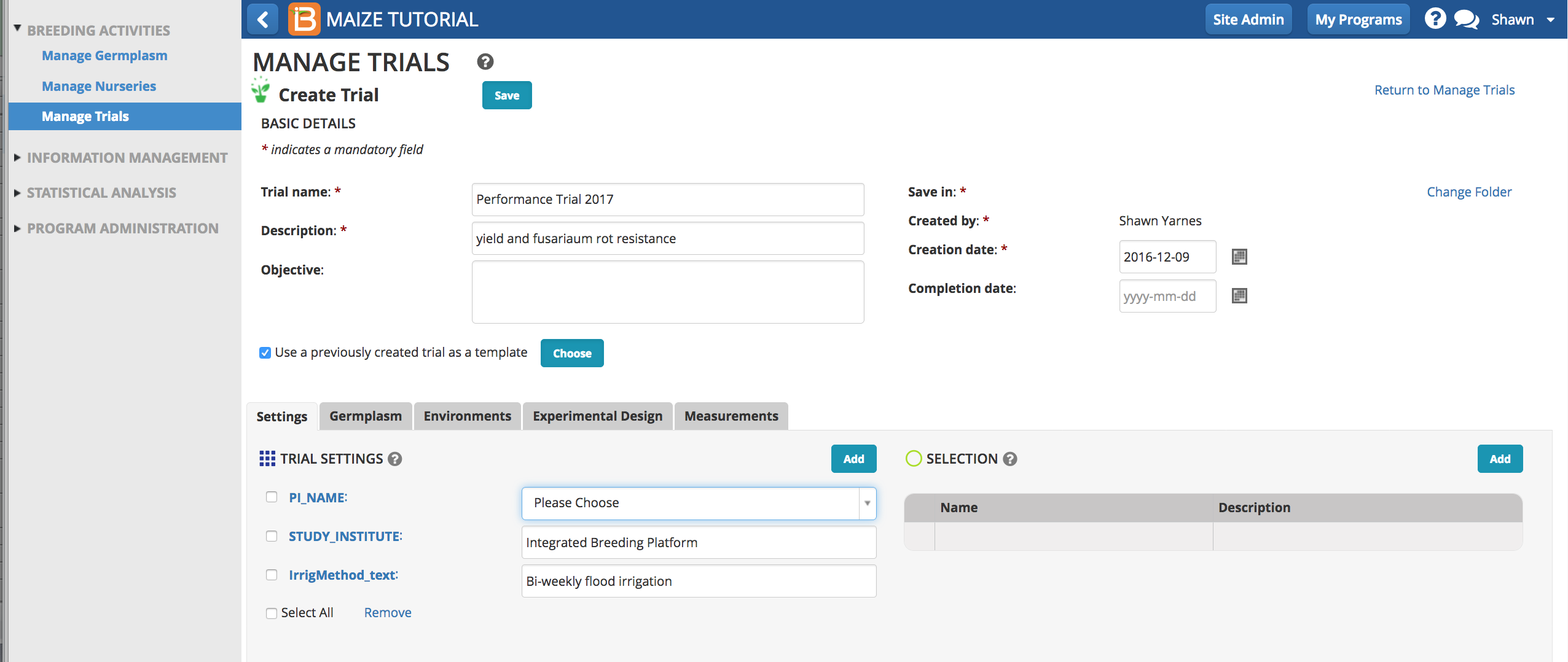
Settings & Selections
Meta-data about the trial can be entered in trial settings. Some setting have pull-down menu options and others allow for free text entry. Some settings are user and program details and others are defined in the crop ontology.
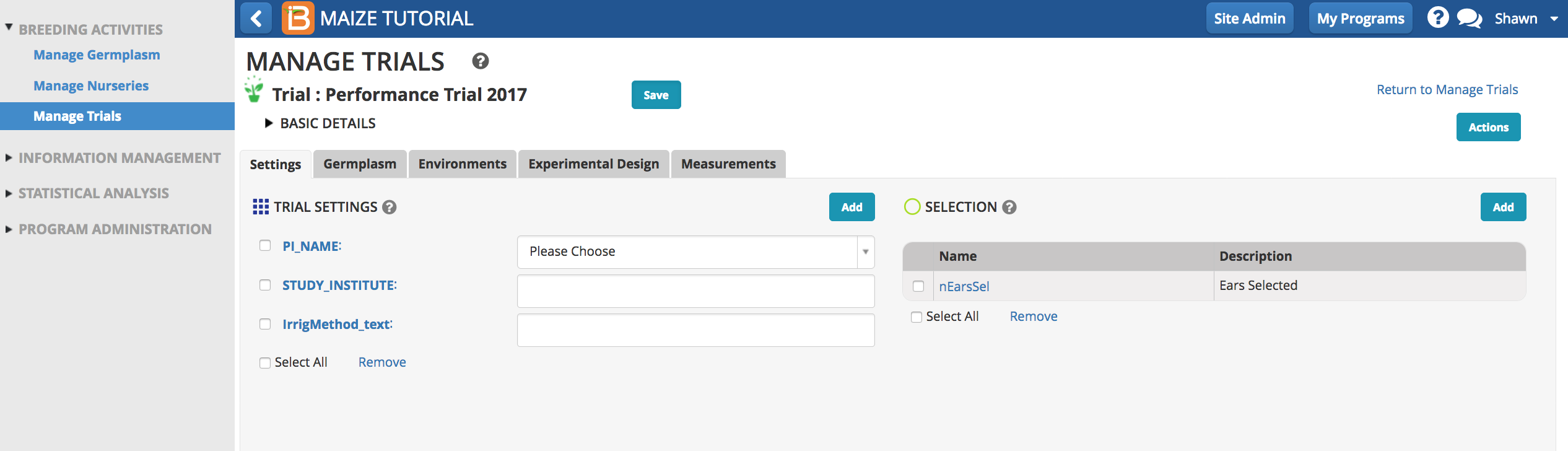
The option to add within plot selection units is also available. For example, a maize breeder may want to select ears from high yielding trial plots for eventual seed increase. See more on advancing trial germplasm.
Add
Select Add to select trial settings and selections. Settings and selection units can be established or modified using the ontology manager.
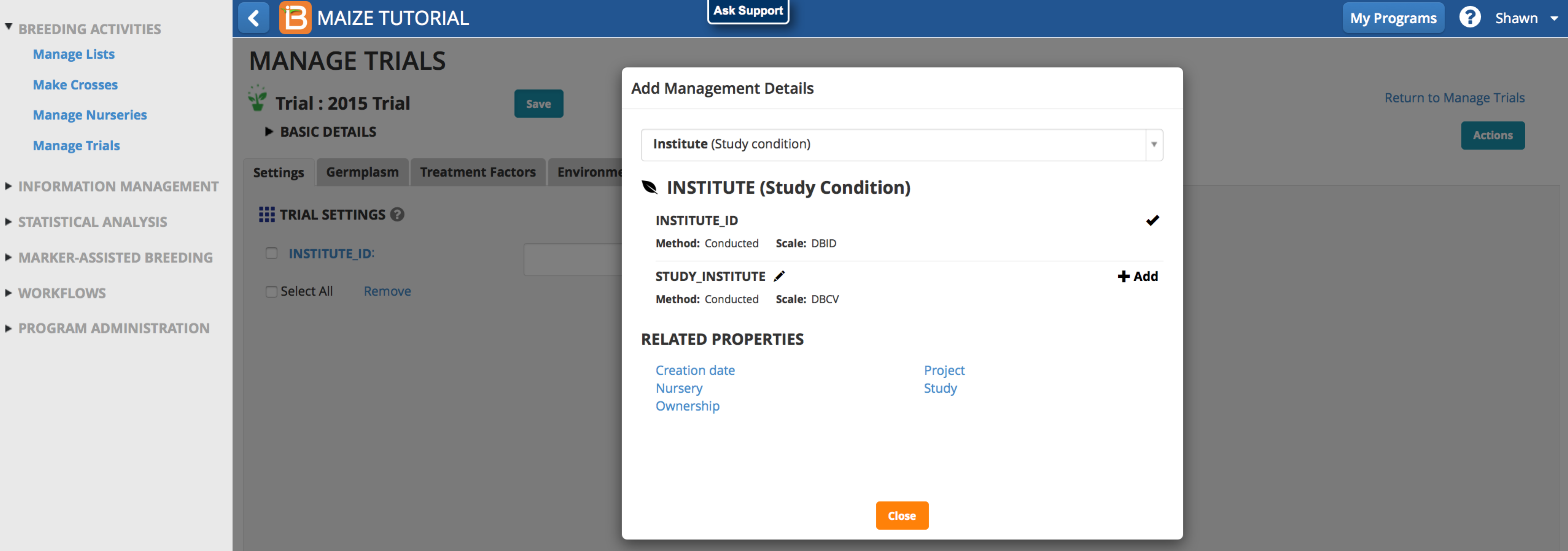
Remove
Remove settings and selections. by checking the box and selecting Remove.
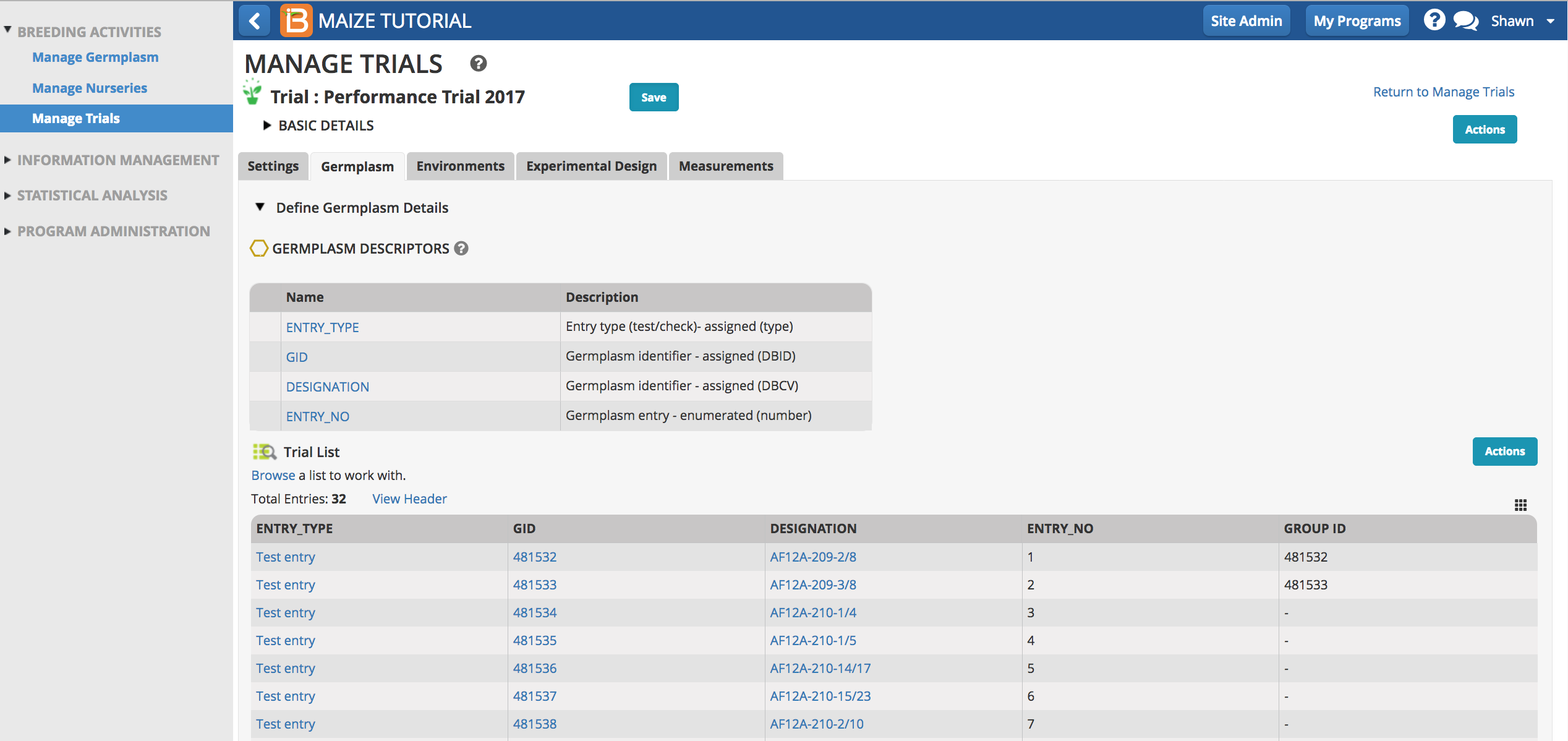
Germplasm
Browse for and upload germplasm list.
Environments
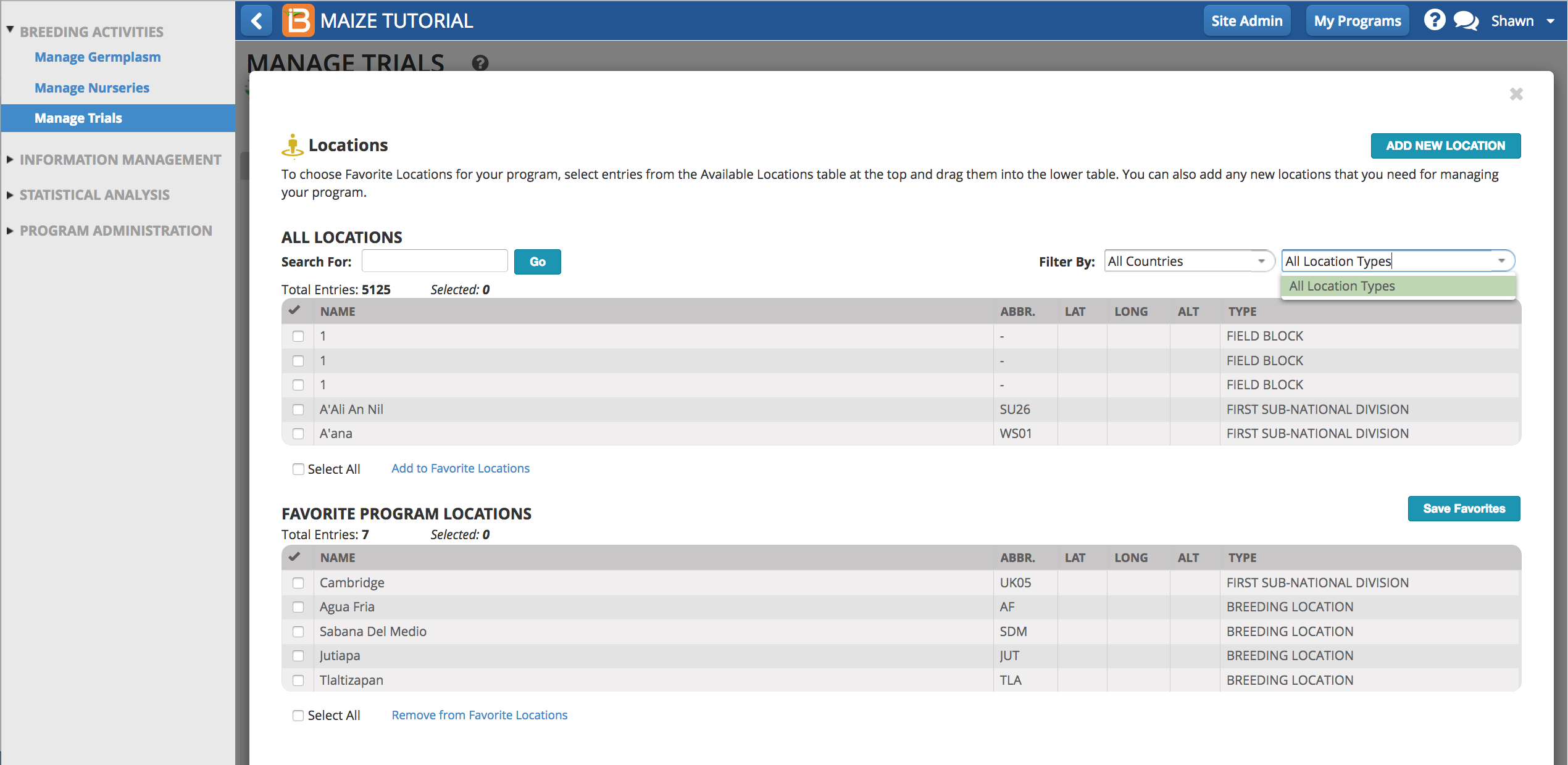
Multiple environments can be specified for a trial (locations and/or seasons). Select Add to select environment details and trial conditions from the crop ontology. New details can be added or modified using the ontology manager. If favorite locations have been specified, checking the Show Favorite Location box will narrow the location options to those relevant to your breeding program.
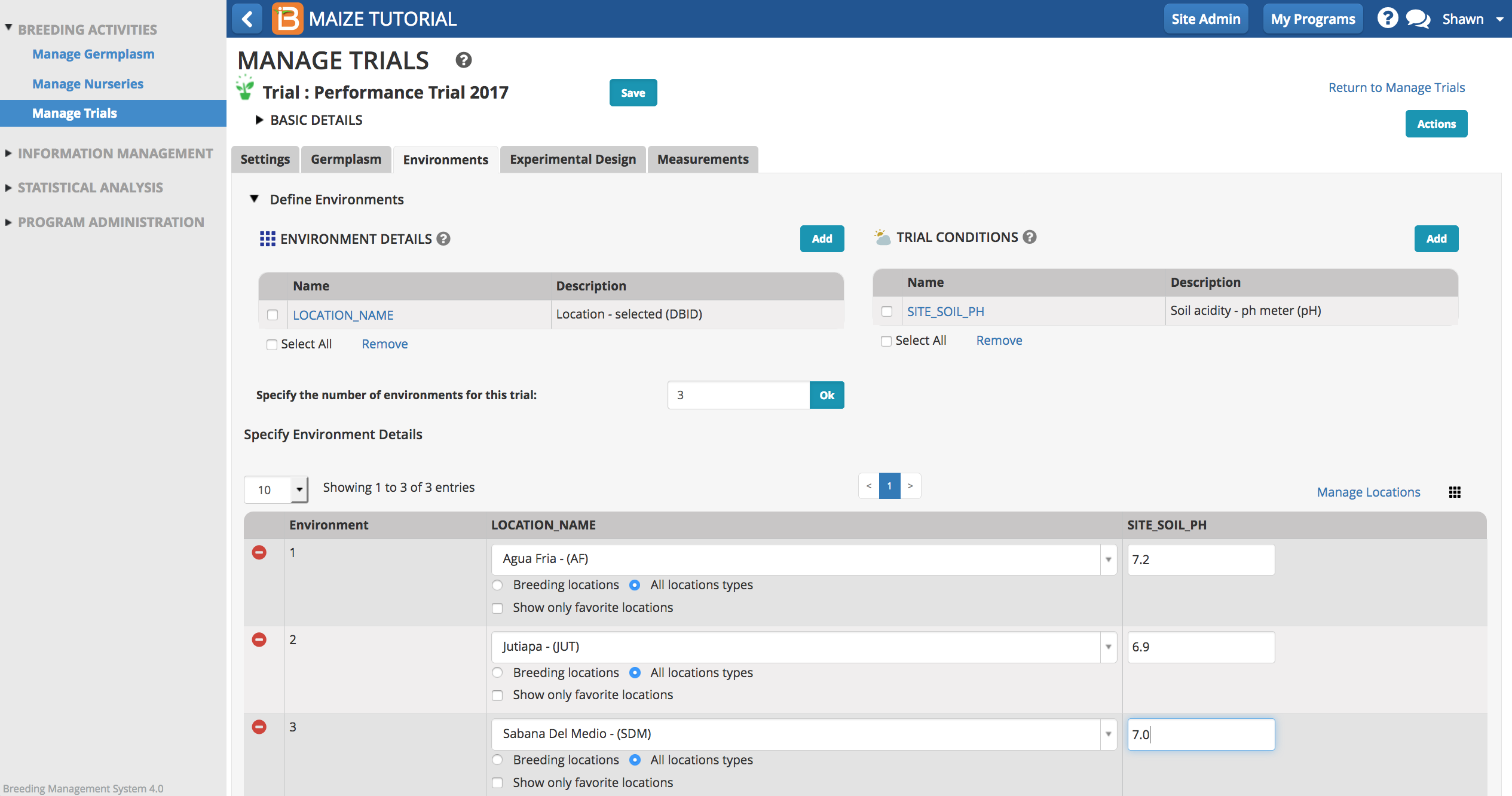
Select Manage Location to customize the programs favorite location list. Depending on user permissions, the Add a New Location button may or may not be available to you. (See more on permissions and location management under Manage Program Settings.)
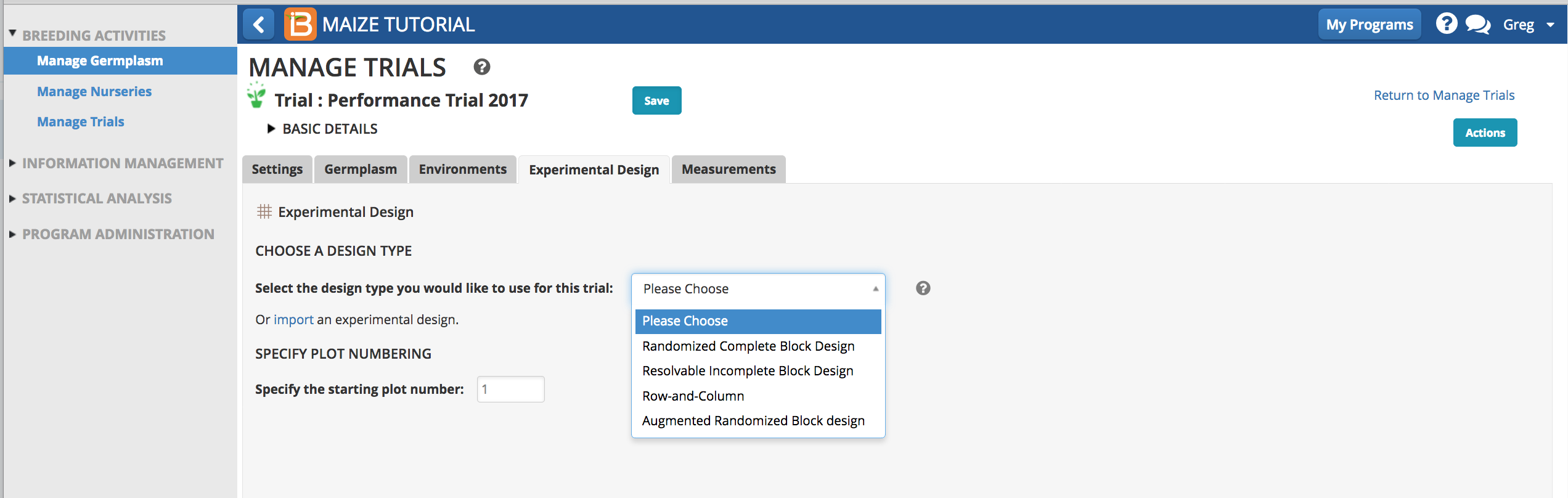
Generate Experimental Design
The BMS can randomize four different experimental designs. After design parameters, like number of replications, are specified, the randomized trial can be generated. The experimental design engine uses ASreml, a proprietary element of the BMS. When you run a design the system checks the license via internet. If you experience an error message about a missing license, please contact your system administrator.
- Randomized Complete Block
- Resolvable Incomplete Block
- Row-and-Column
- Augmented Randomized Block
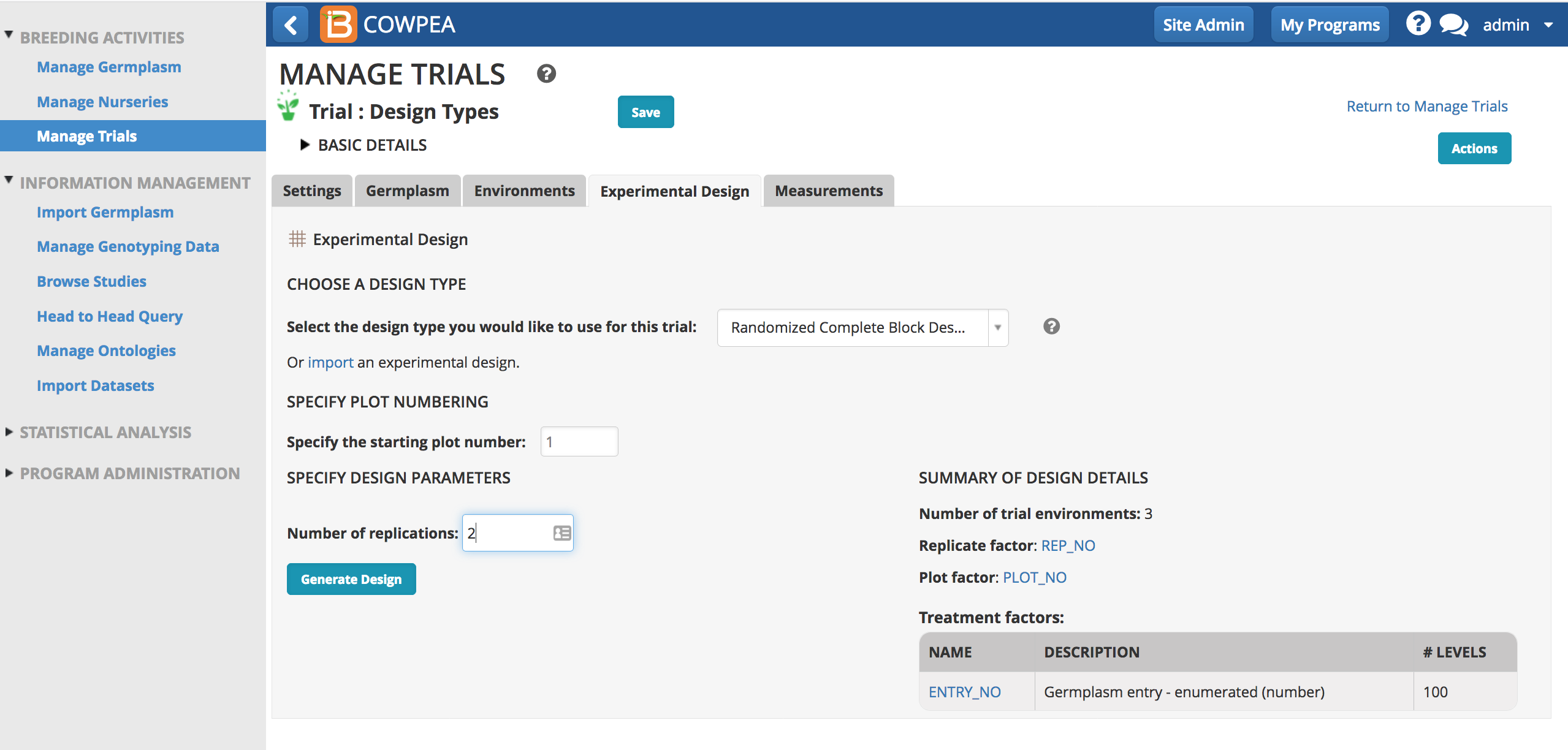
Randomized Complete Block Design
The simplest blocked design is the Randomized Complete Block (RCB) design. In this design each of the v, treatments occurs once in every block (or replicate), and the number of units per block, k, is constant and equal to the number of treatments (v = k). These characteristics result in a balanced dataset, and therefore, any treatment comparison has the same precision.
- Select Randomized Complete Block design as the experimental design. Enter the number of desired replications and select Generate Design.
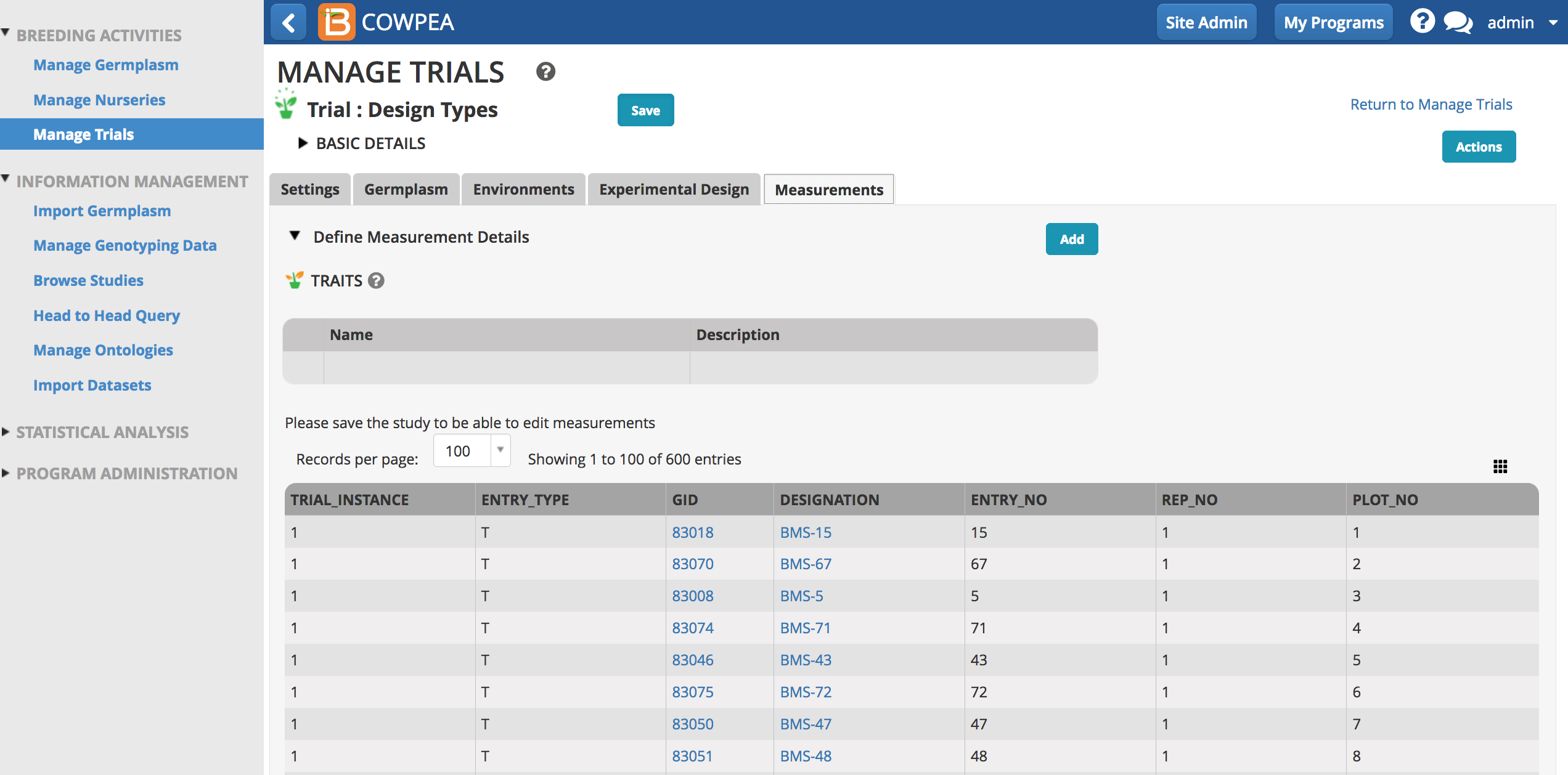
- After receiving a success message, the Measurements table is now populated with a randomized complete block design.
Resolvable Incomplete Block Design
In a resolvable Incomplete block design plots are grouped into blocks that are not large enough to contain all germplasm (treatments), and resolvable blocks are created by grouping incomplete blocks together, so that each treatment is replicated exactly once in each group or set.
- Select Resolvable Incomplete Block Design as the experimental design. Enter the number of desired replications. Enter the number of blocks - number of blocks must be a factor of the number of treatments. Select Generate Design.
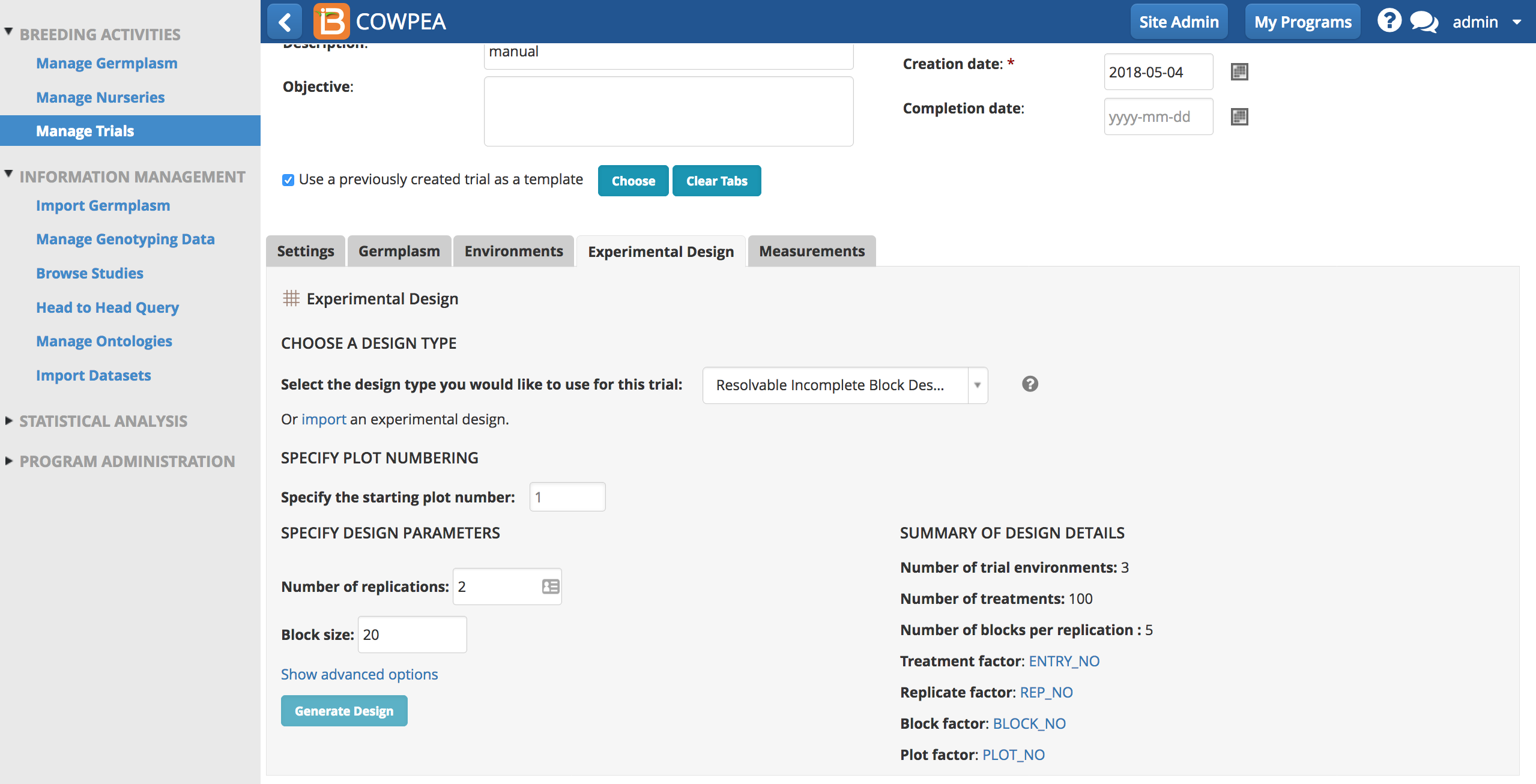
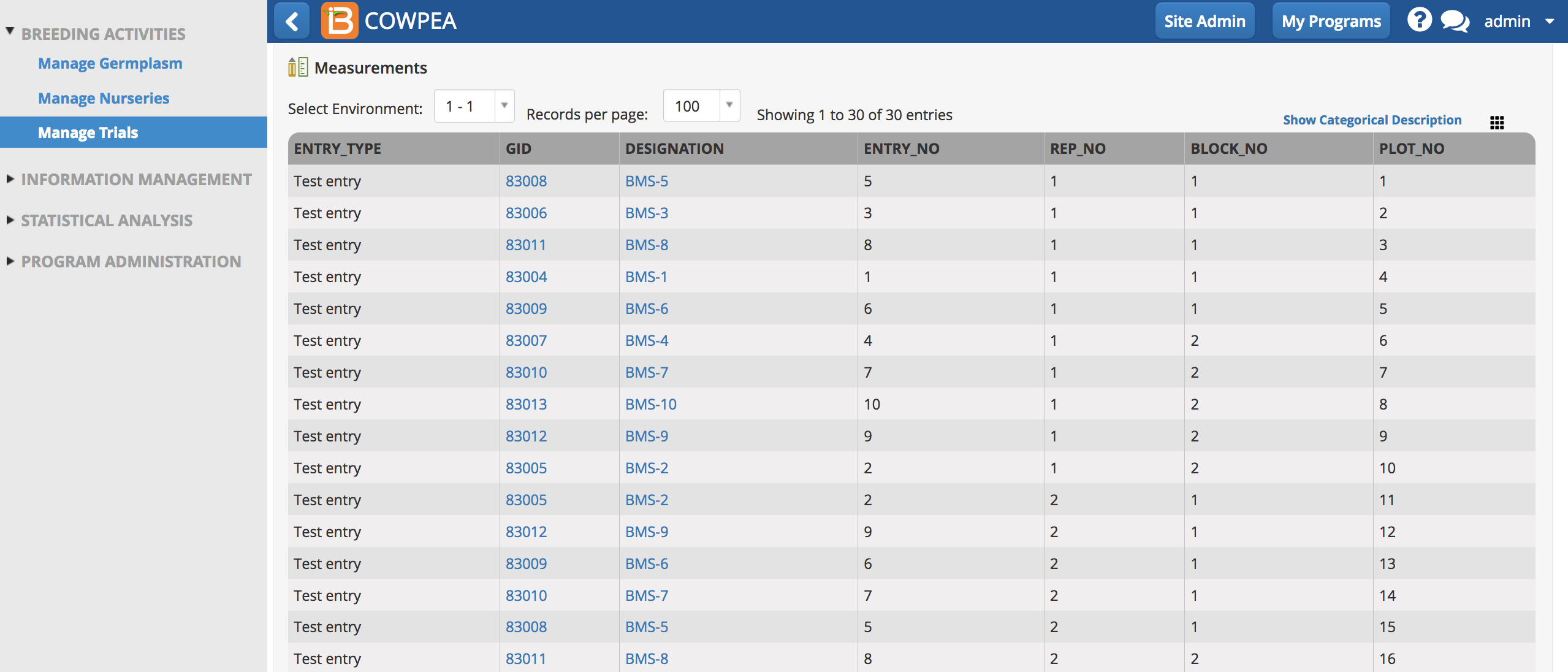
After receiving a success message, the Measurements table is now populated with a resolvable complete block design.
Row-And-Column Design
When the heterogeneity is known or suspected in two directions (rows and columns), Row-and-Column (RC) designs can be used to group experimental units in two directions. The purpose of a RC design is to eliminate equally from the errors all differences among rows and among columns. Under these situations, the experimental material should be arranged and the experiment conducted so that the differences among rows and columns represent major sources of variation.
- Select Row-And-Column Design as the experimental design. Enter the number of desired replications. Enter the number of row and columns within the replications. The number of rows multiplied by the number of columns must equal the number of treatments. Generate Design.
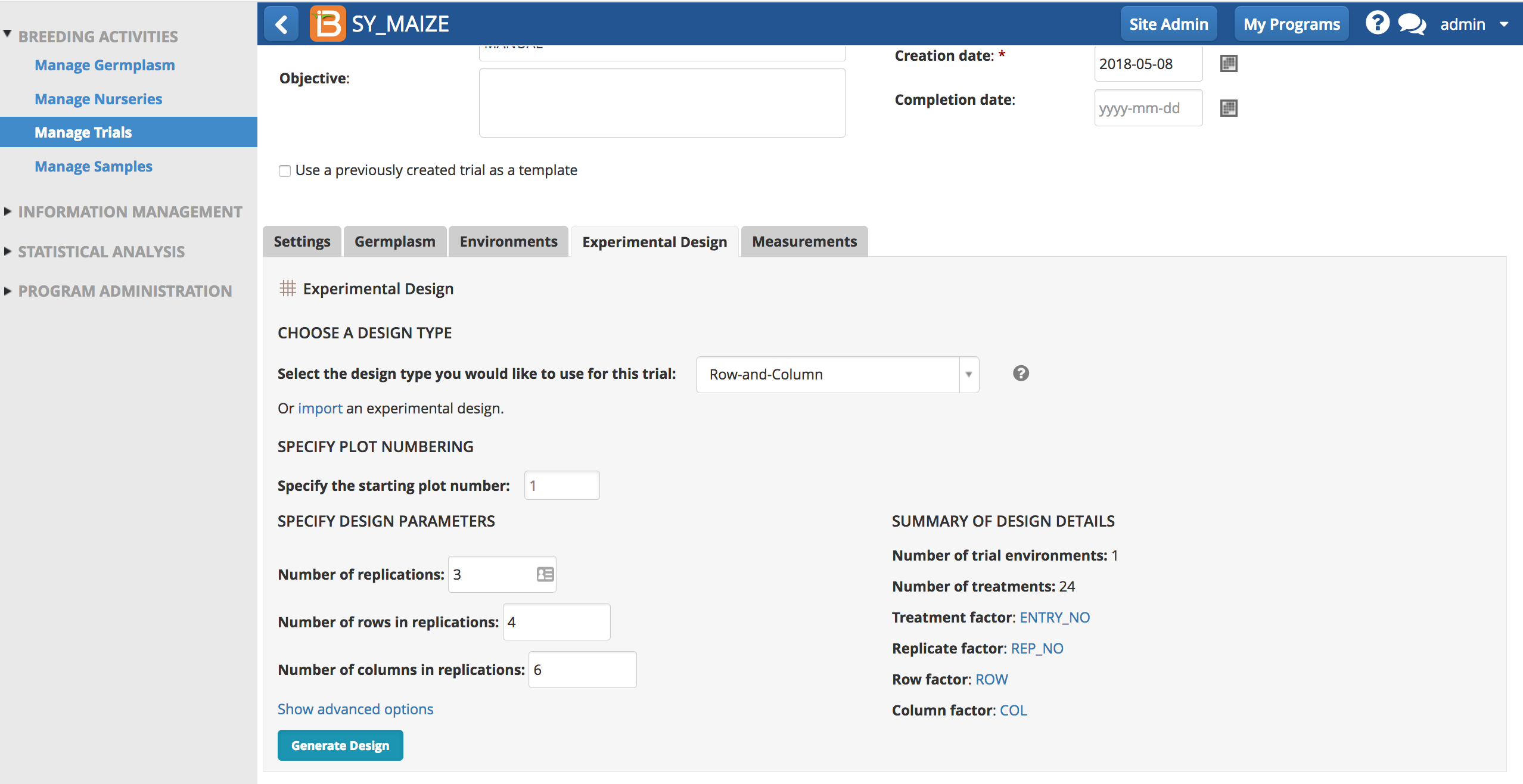
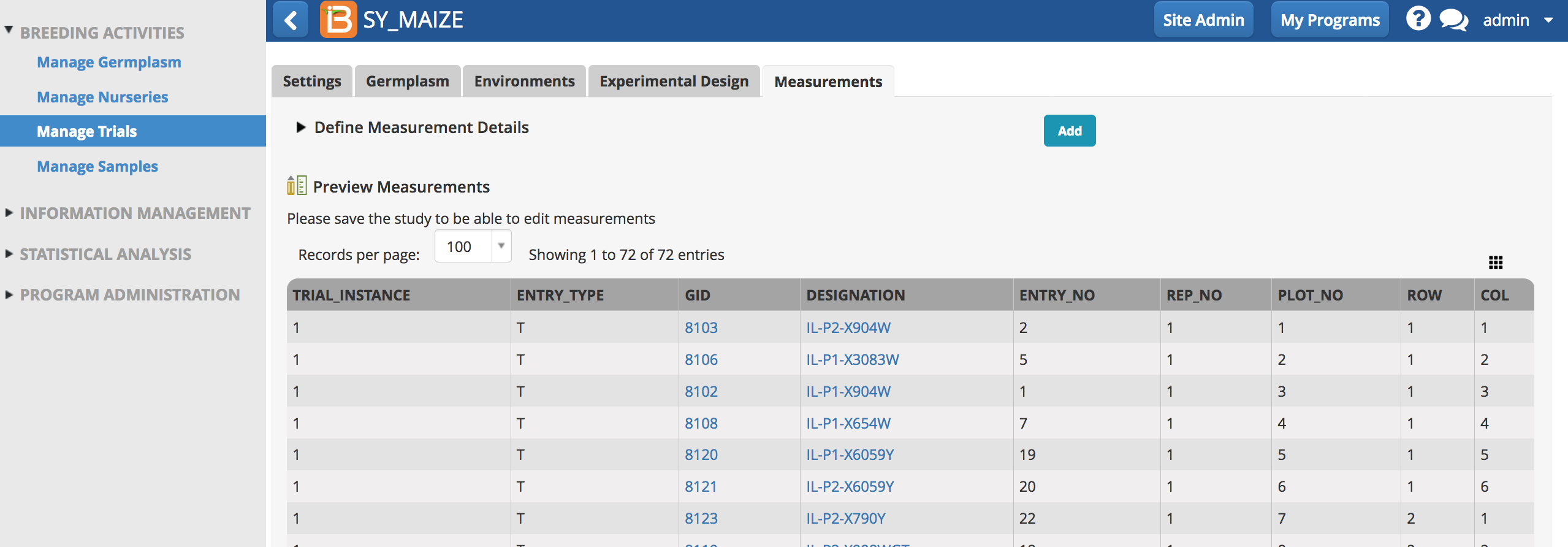
After receiving a success message, the Measurements table is now populated with a Row-and-Column design.
Augmented Randomized Block Design
Augmented Randomized Block Design is constructed using control or "check" entires for which there are sufficient seed to allow several replications. The number of available experimental plots in each replication may vary, but all of the checks are included at least once; the remaining plots are assigned to the new or "test" entries. Performance of the checks can be used to adjust the performance of the test entries to make them comparable across replications and to provide an estimate of experimental error so that valid statistical tests can be performed.
- Specify check entries in the germplasm tab. By default all entries are "test".
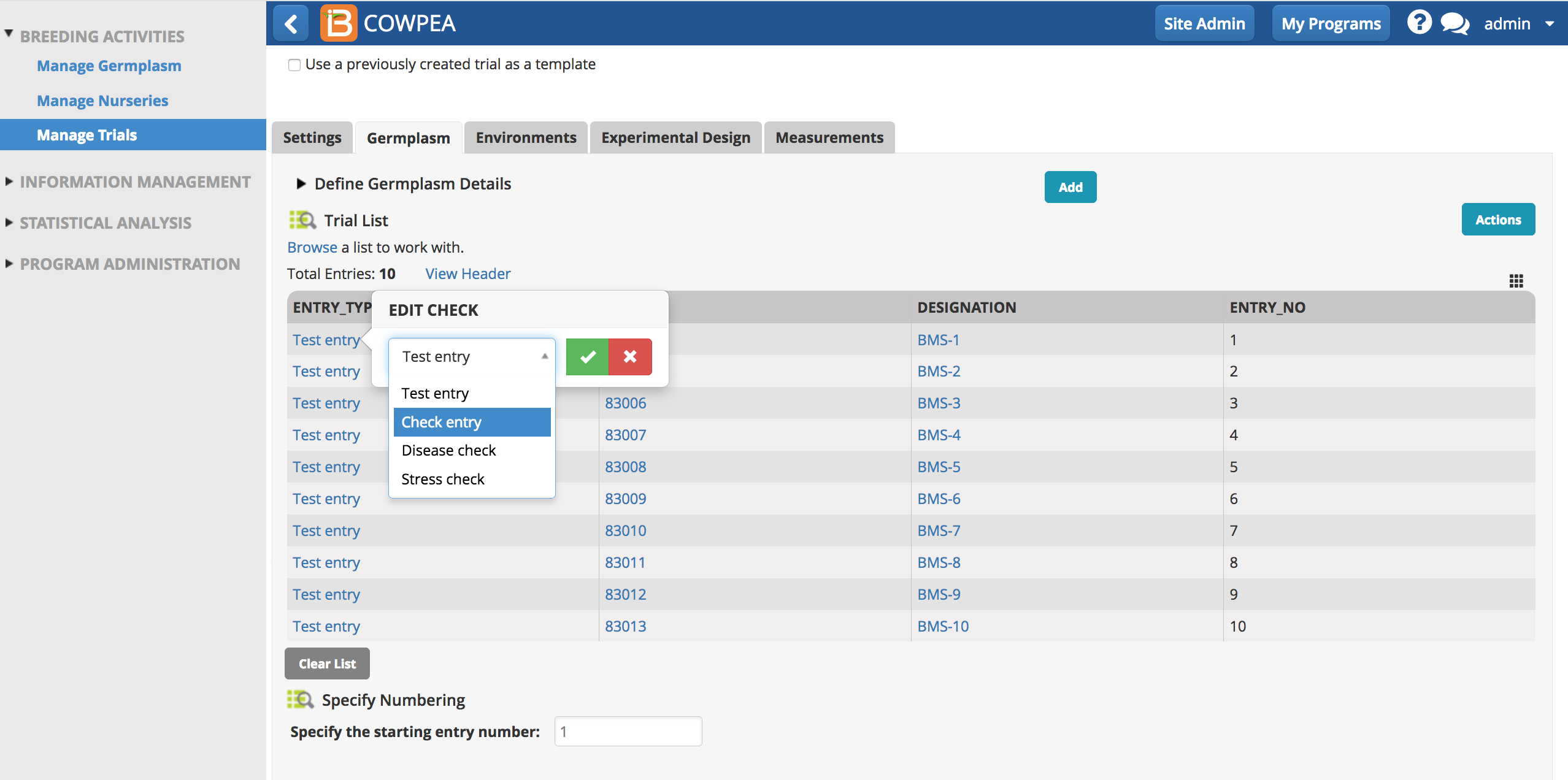
The number of experimental blocks must be a factor of the number of test entries.
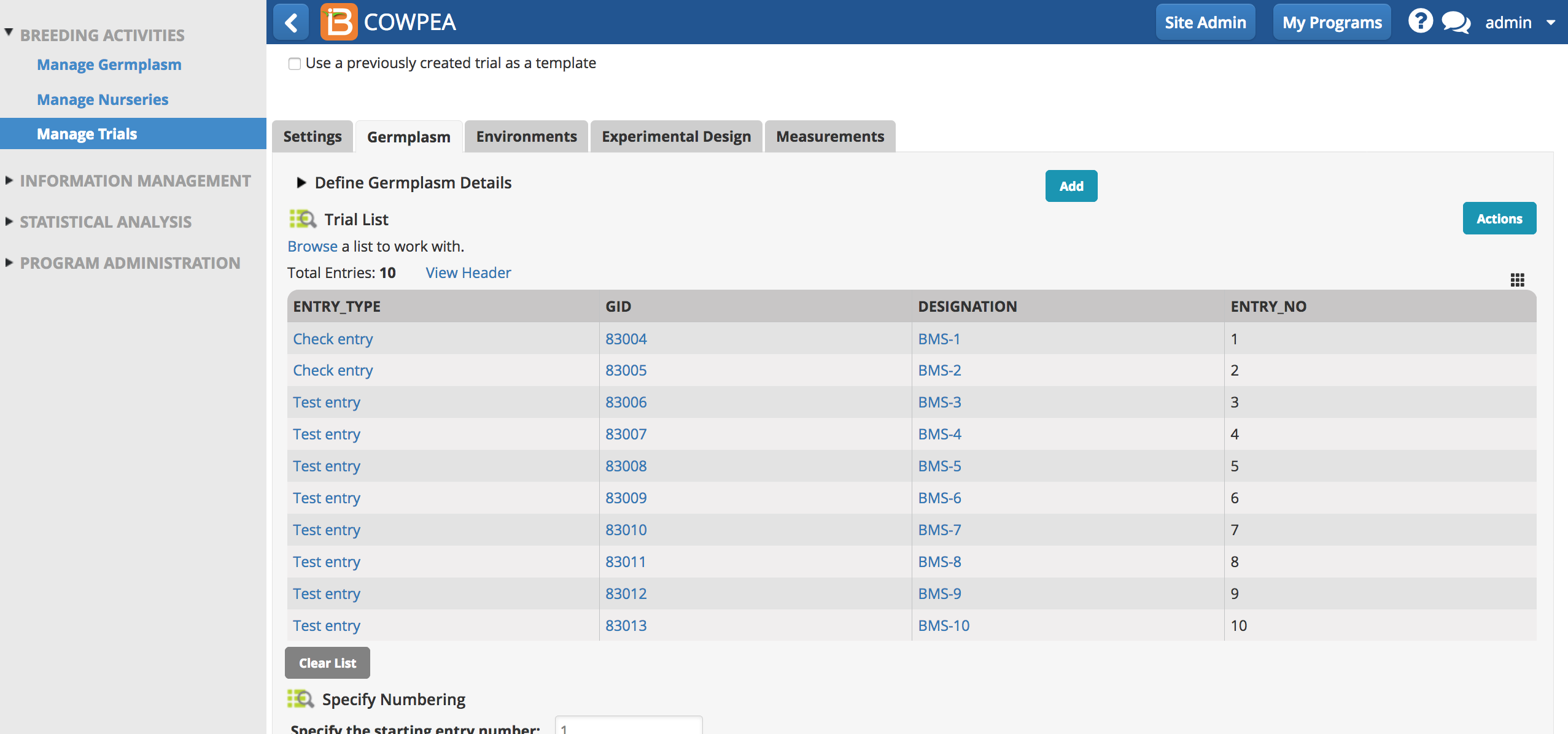
In this example, there are 2 check entries and 8 test entries. Factors of 8 (1, 2, 4, and 8) are options for block number in the experimental design.
- Specify Augmented Randomized Block Design and enter the number of desired blocks. Generate design.
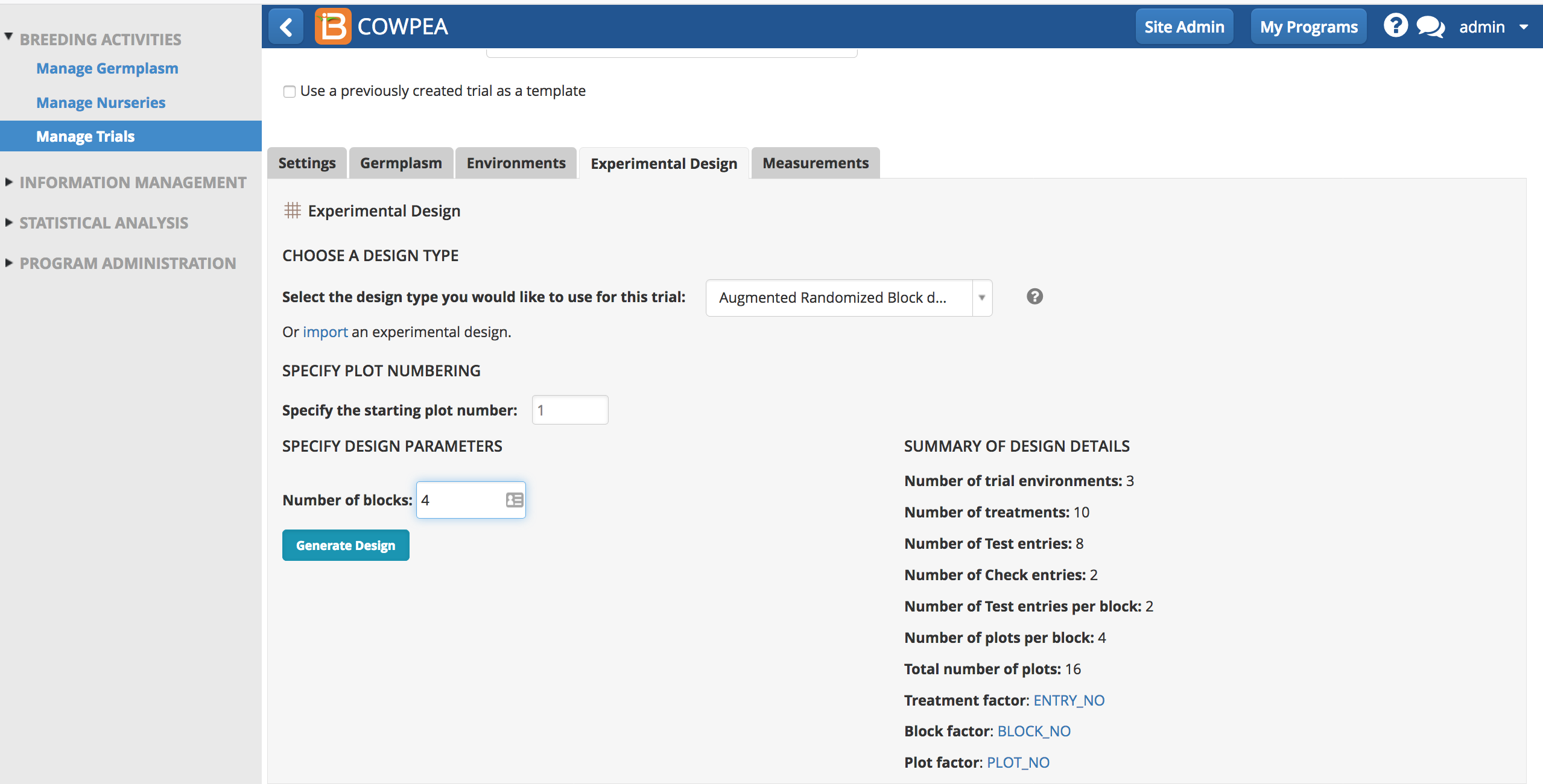
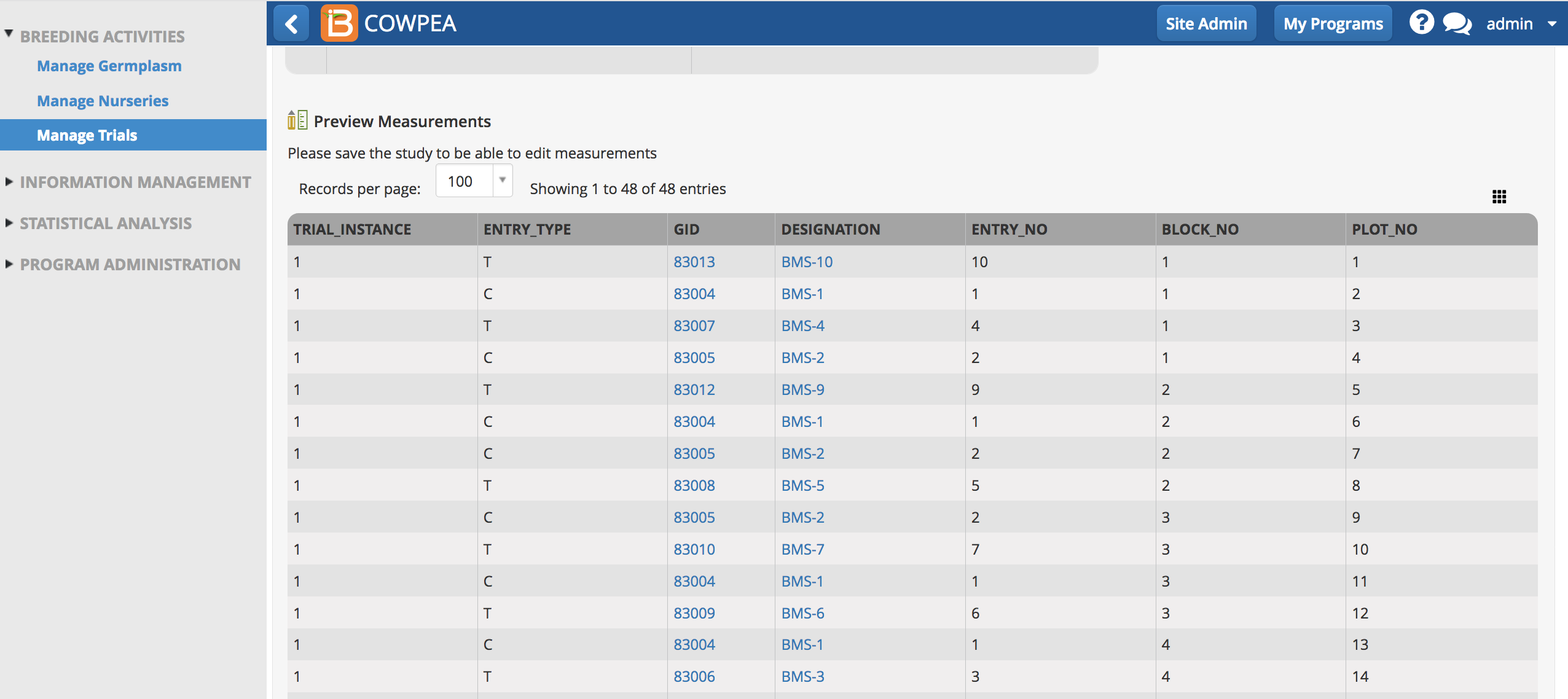
After receiving a success message, the Measurements table is now populated with an augmented randomized block design.
Import Experimental Design
Import custom trial design files (.csv) generated outside of the BMS. Randomizations created outside of the BMS may not be supported by BMS statistical analyzes, but users have the flexibility to use external statistics applications if desired.
- Export Design Template.
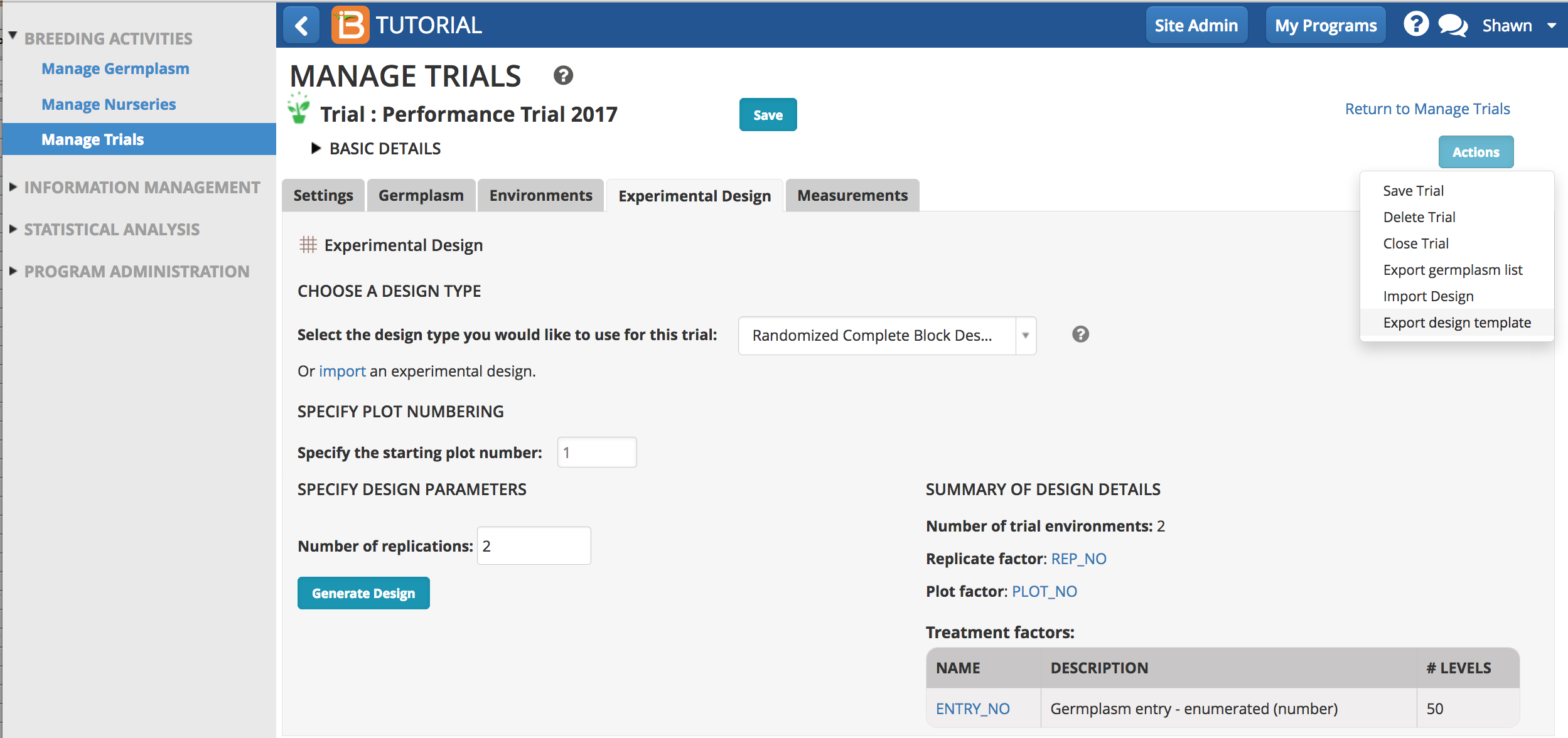
The exported design template (.csv) contains the 3 mandatory column headings
- TRIAL_INSTANCE: Number corresponding to specific trial environments, like a particular location or season.
- ENTRY_NO: Number corresponding to specific germplasm. The number of entries in the trial design file must equal the number of entries in the trial germplasm list.
- PLOT_NO: Plot number
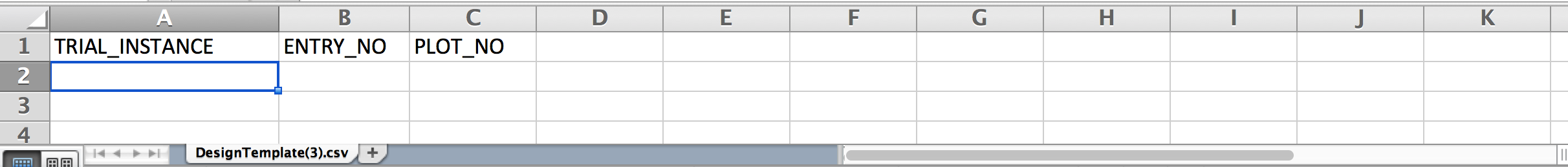
- Edit the design template. Some experimental designs will require the addition of other optional columns.
- Select Import an Experimental Design.
- Specify the design file and Continue.
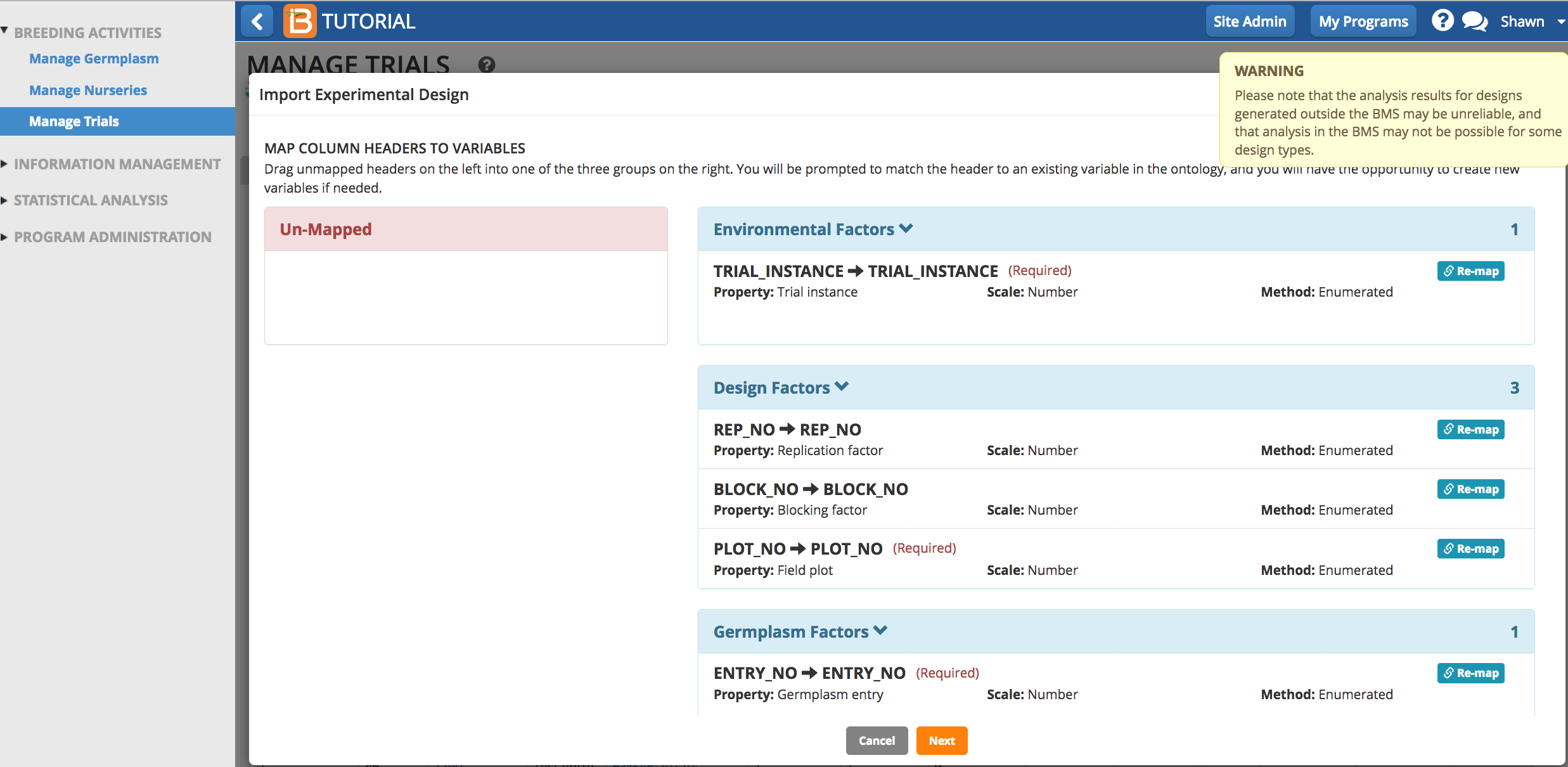
Ontology terms in the design file that are identical to the ontology will map perfectly. If the column headers are spelled differently, the system will attempt to map to match the existing ontology. You may be required to Re-map and/or add new ontology terms to achieve correct mapping.
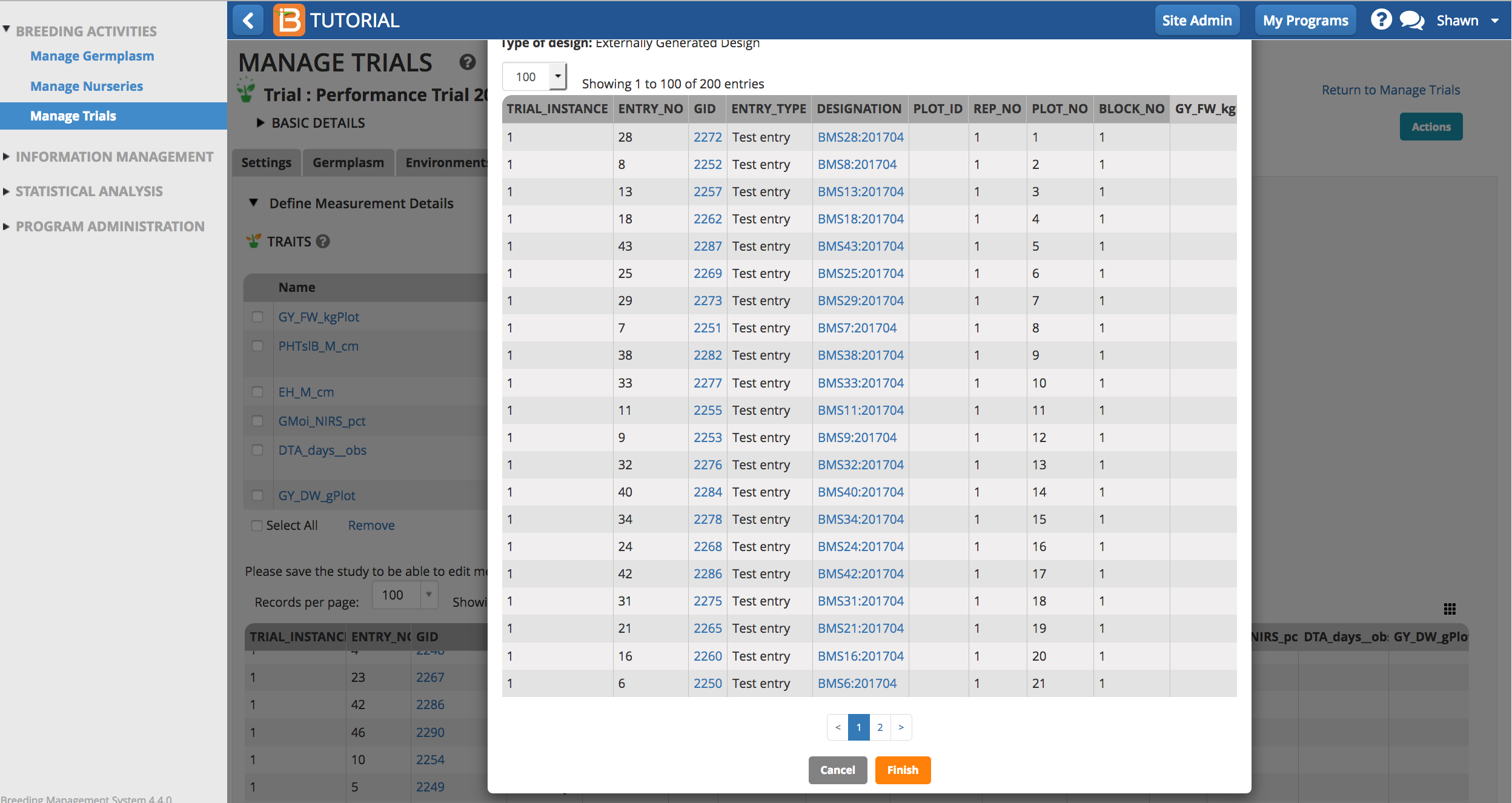
Review imported design details and select Finish.
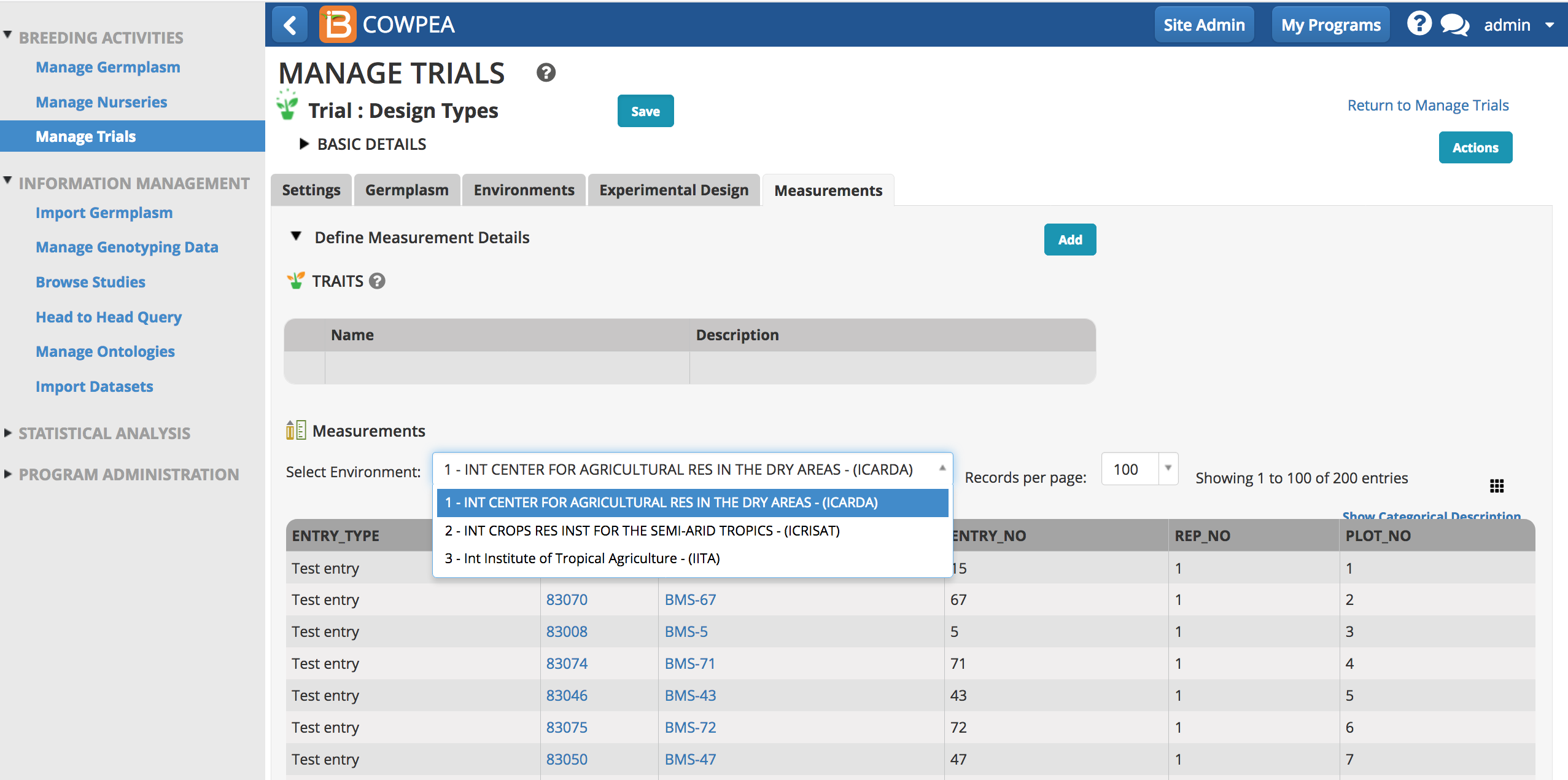
Measurements
Once the experimental design has been generated or imported, the Measurements tab is populated with independent trial variables.
- Save the trial and the measurements table will become paginated by trial instance (location in this example).
Unique Plot ID
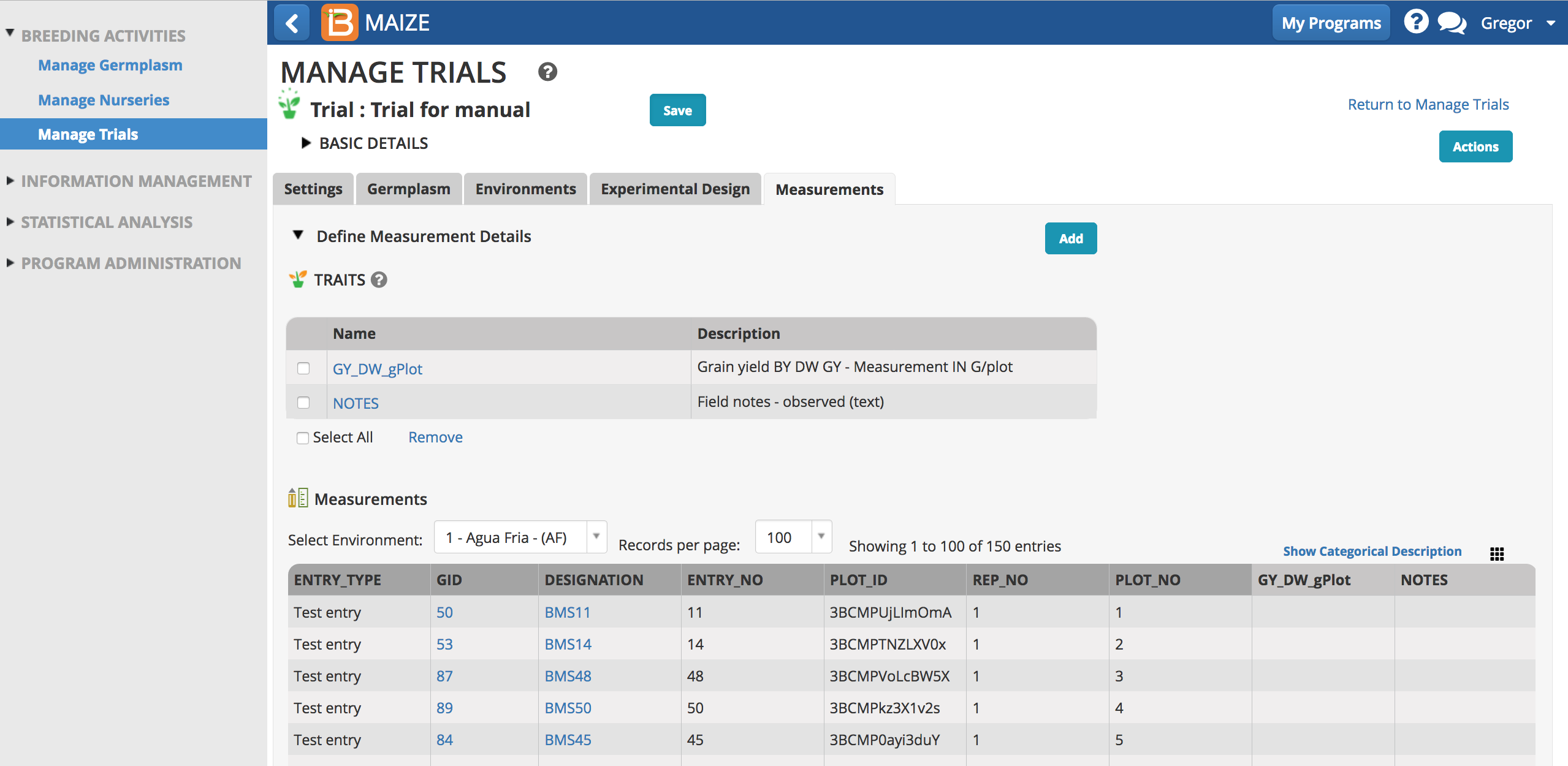
The column of unique plot IDs is hidden by default. You can add this column of data by selecting the dotted rectangle and selecting PLOT_ID.
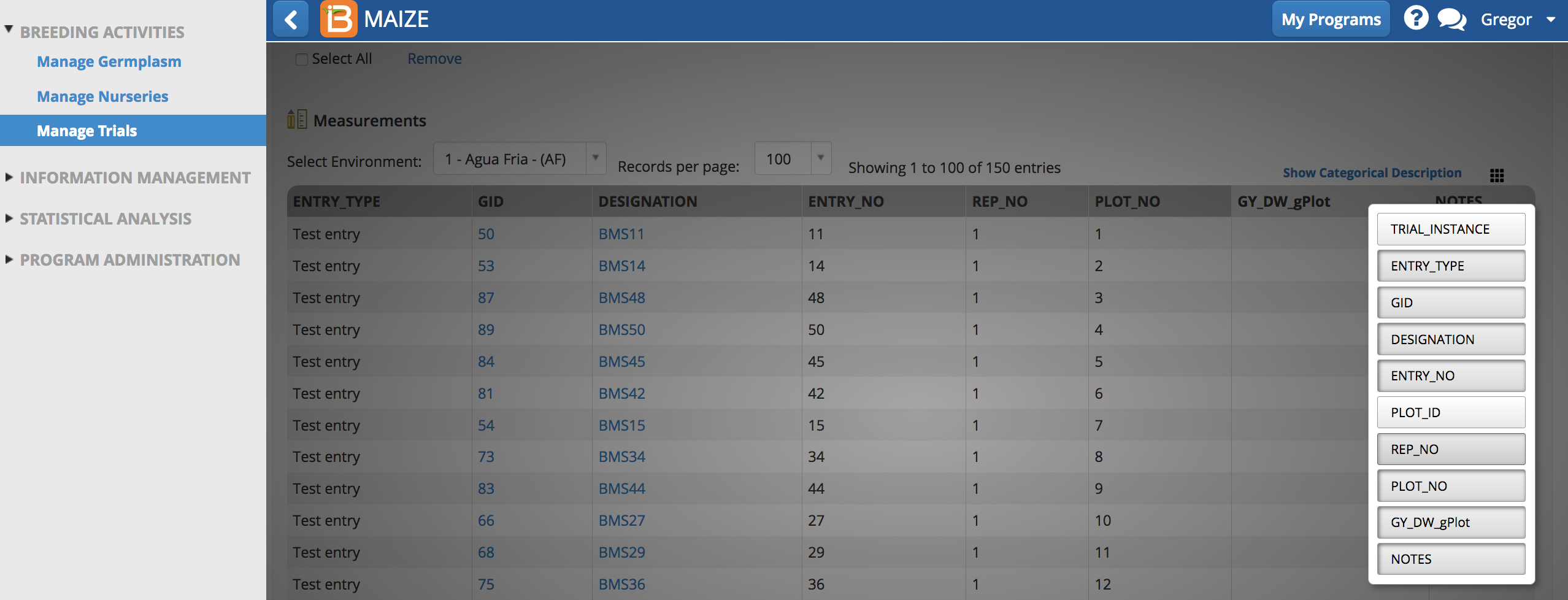
PLOT_ID is an alphanumeric sequence designed for data capture that uniquely identifies the plot.
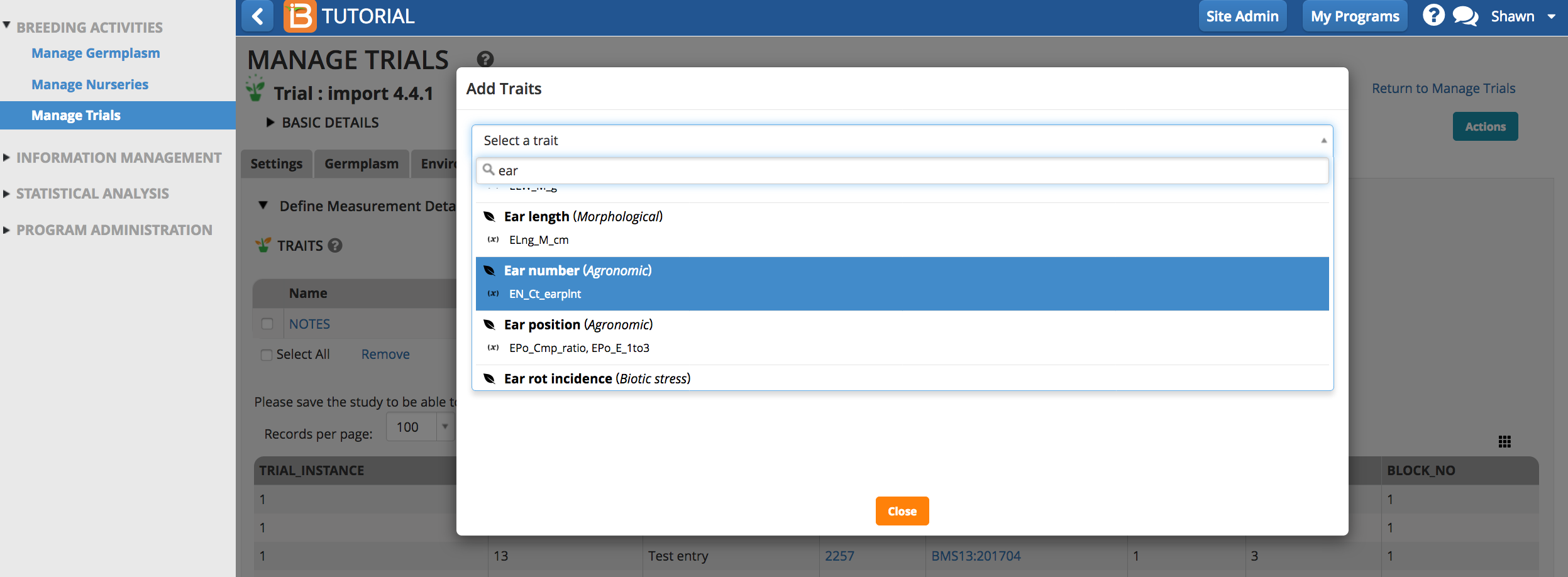
Add Traits
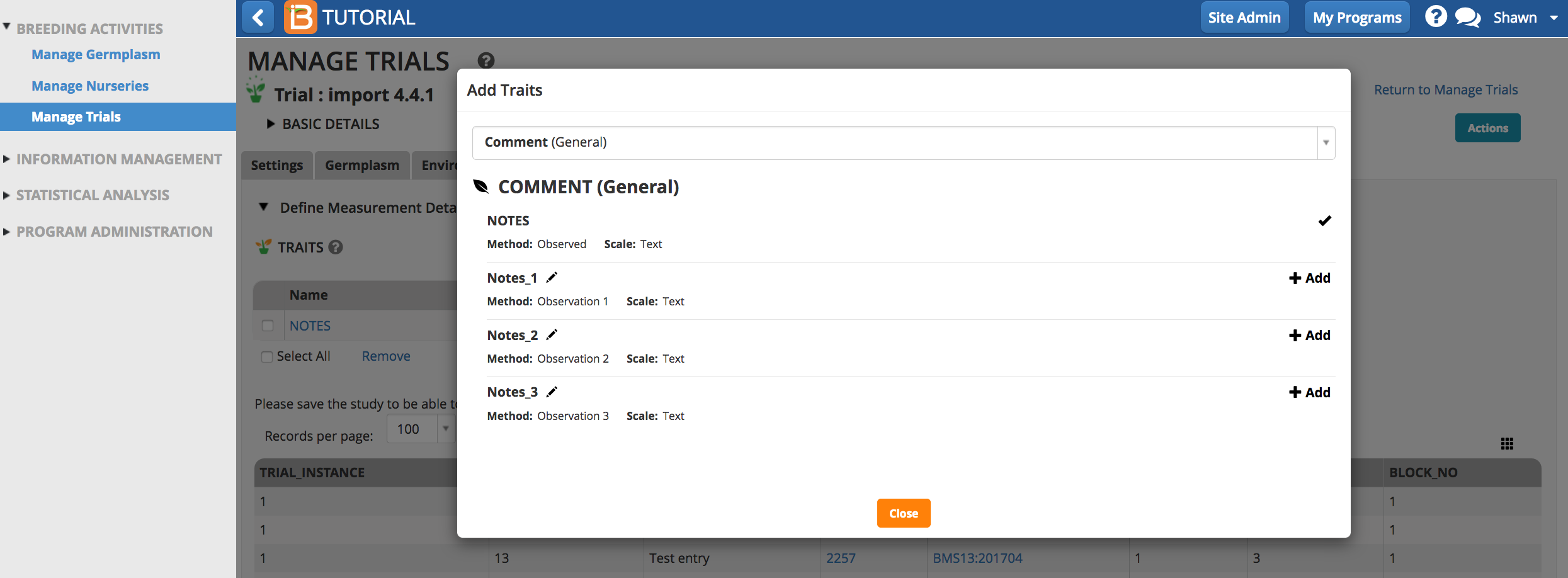
- Select the Add button to specify traits to measure, or the dependent variables.Type a word or part of a word that describes the trait that will be measured. If the desired trait cannot be found, the new trait must be added to the crop ontology.
Once selected the trait of interest will appear as an empty column of data in the measurements table.
Once saved, the trial is available for many other activities.
- Export Trial Book (Same as described in Manage Nurseries)
- Make Field Map
- View Field Map
- Create Planting Labels
- Import Measurements (Same as described in Manage Nurseries)
- Advance Trial
- Save Trial
- Delete Trial
- Close Trial
- Add Environments
- Export Germplasm List
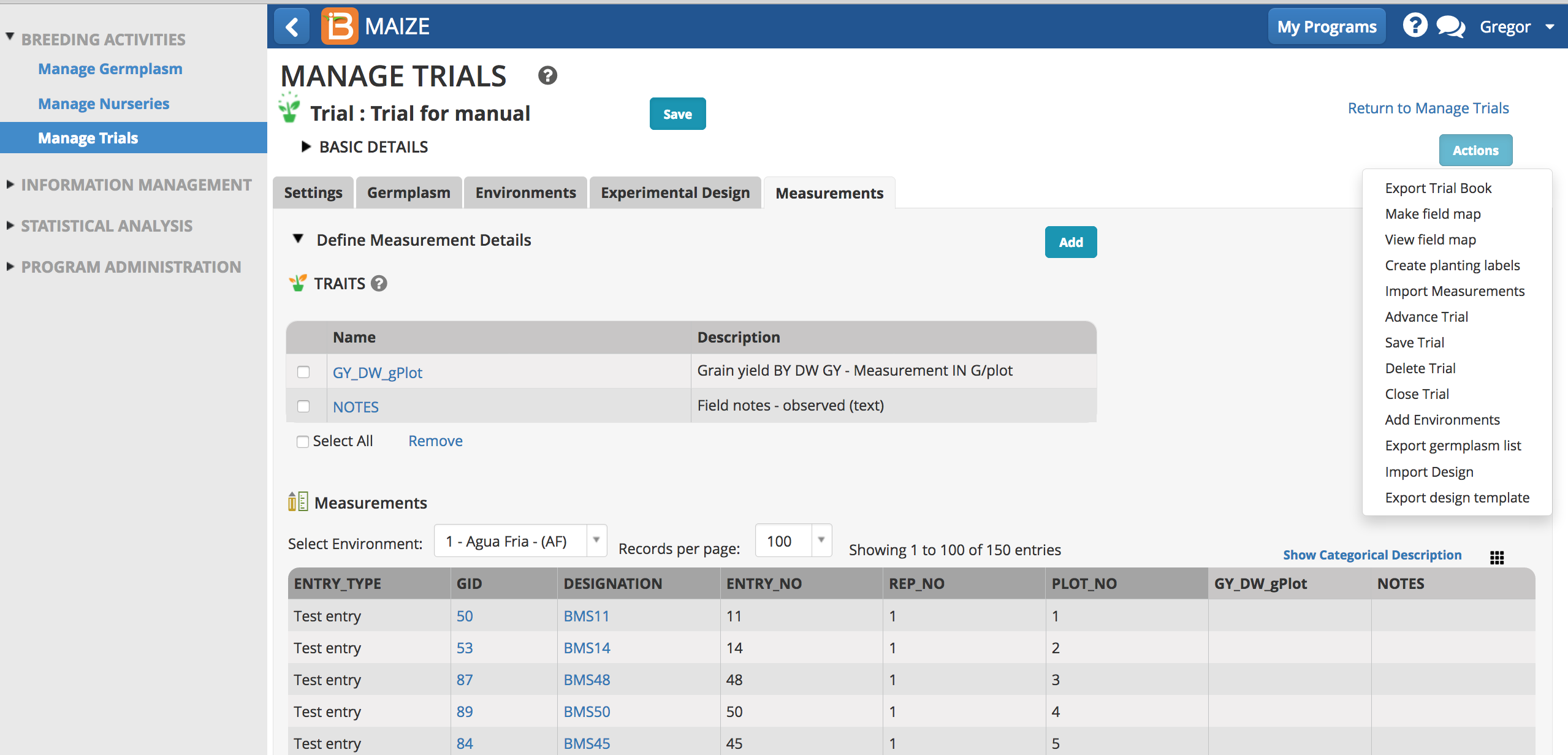
Export Data Collection File
Same as described in Manage Nurseries
Import Data Collection File with Measurements
Same as described in Manage Nurseries
Advance Trial
Advance offspring from trial germplasm.
- Select Advance Trials from the Actions menu.
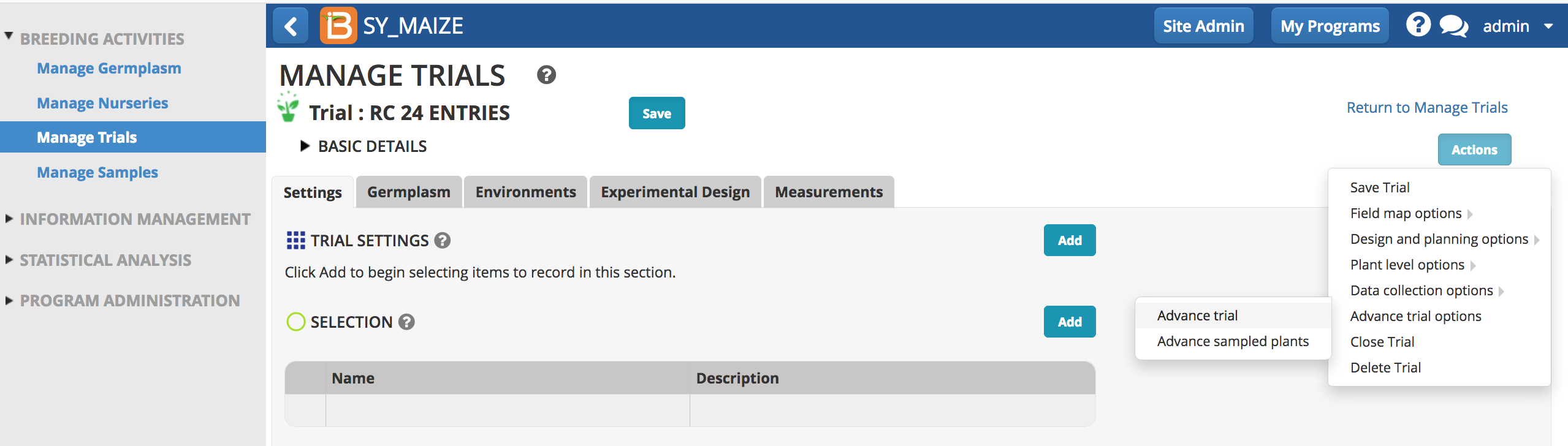
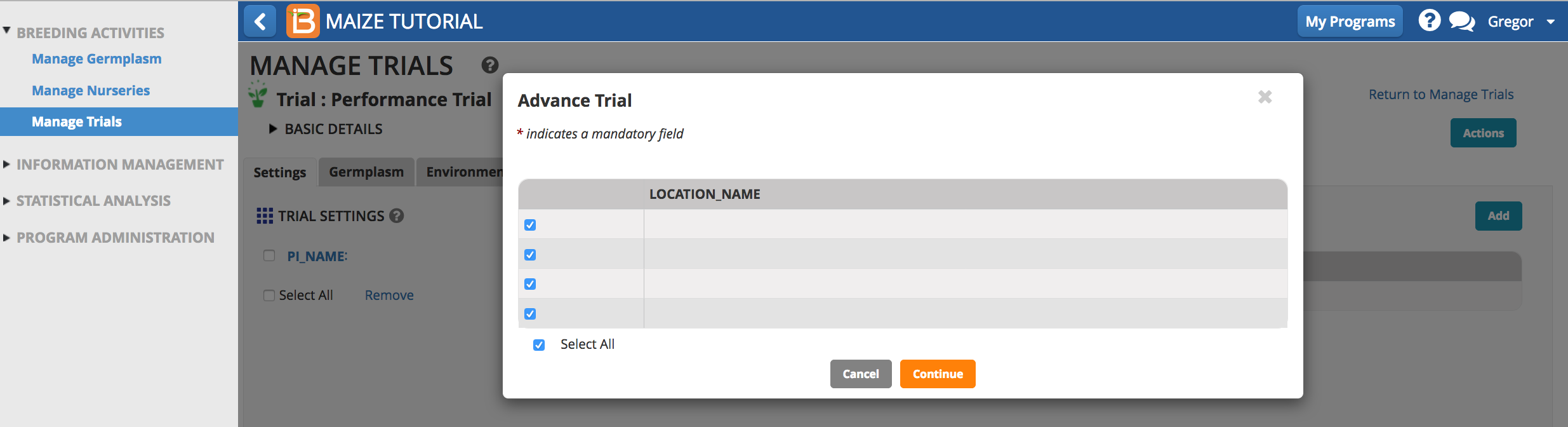
- Specify the trial locations to advance.
- Select the breeding method. Either choose a selection unit or the number of lines per plot. Select Finish.
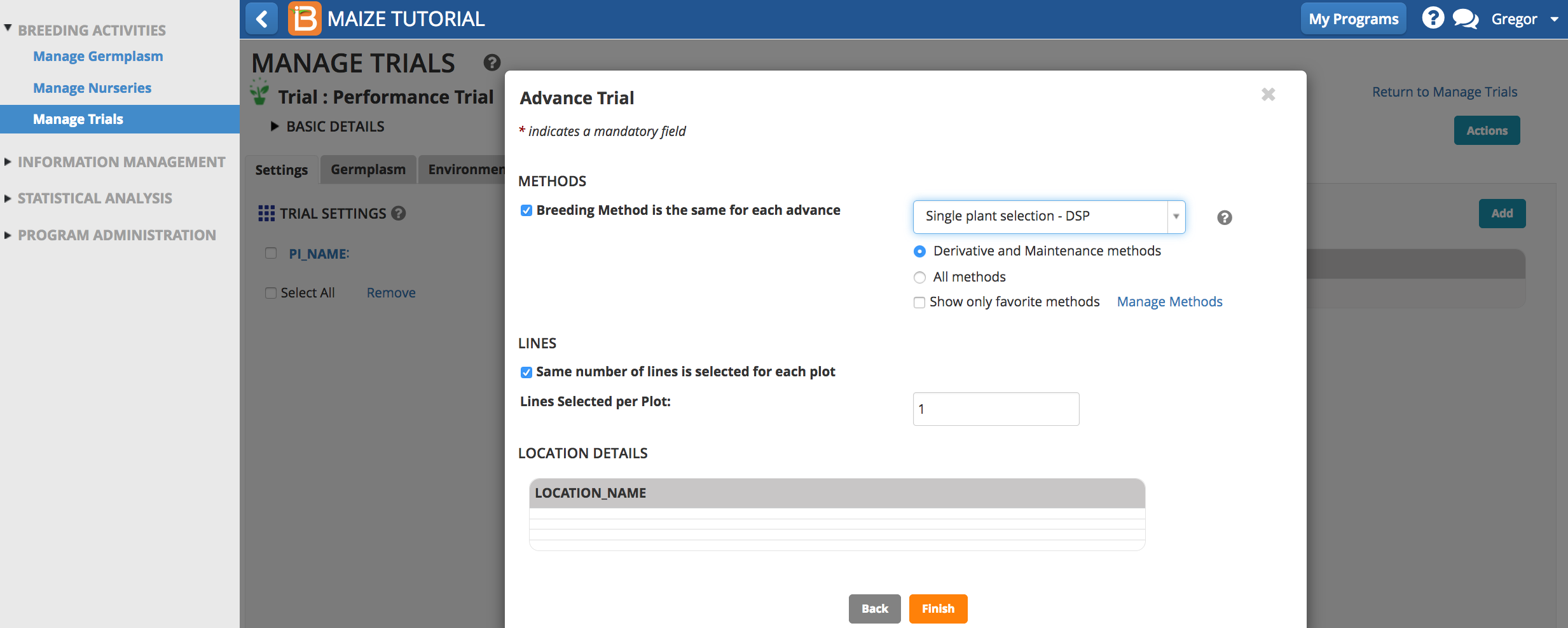
- Review the advances lines and Finish.
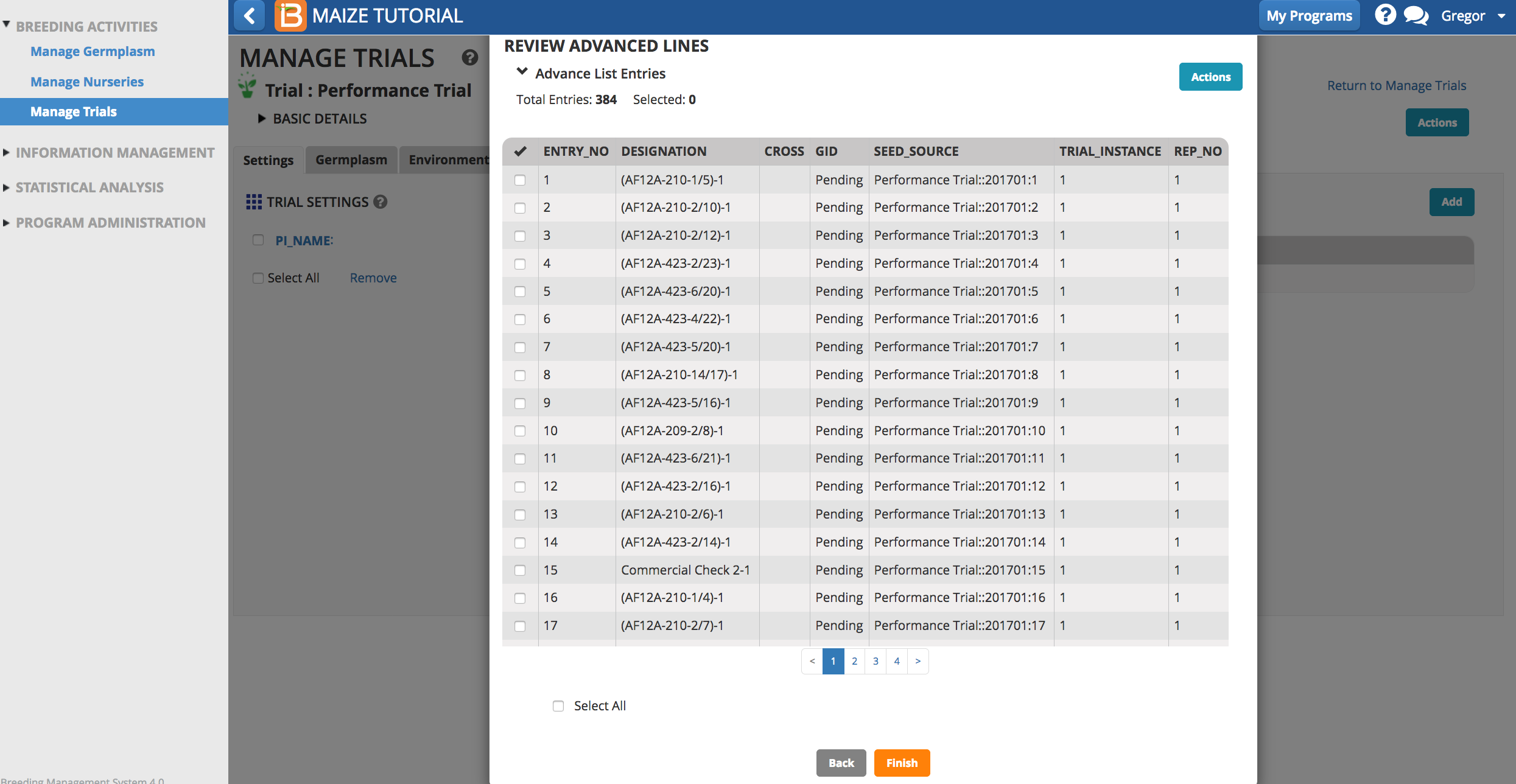
- Save the advance list of germplasm.
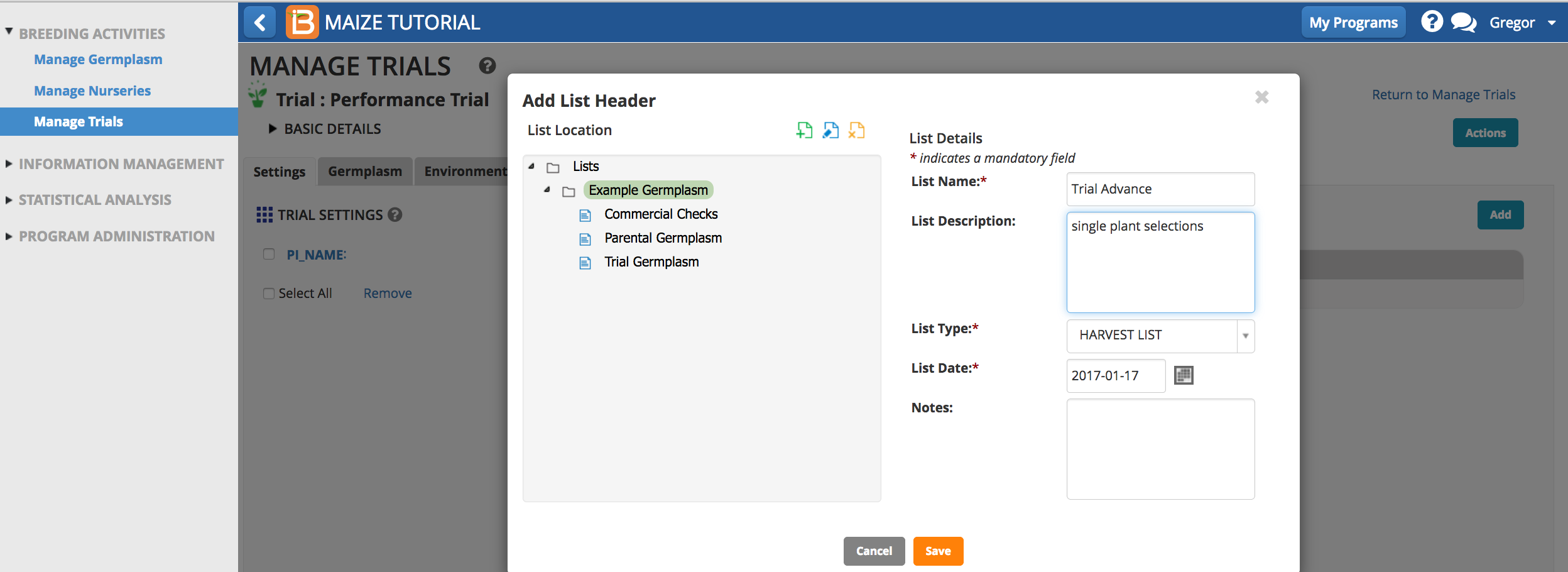
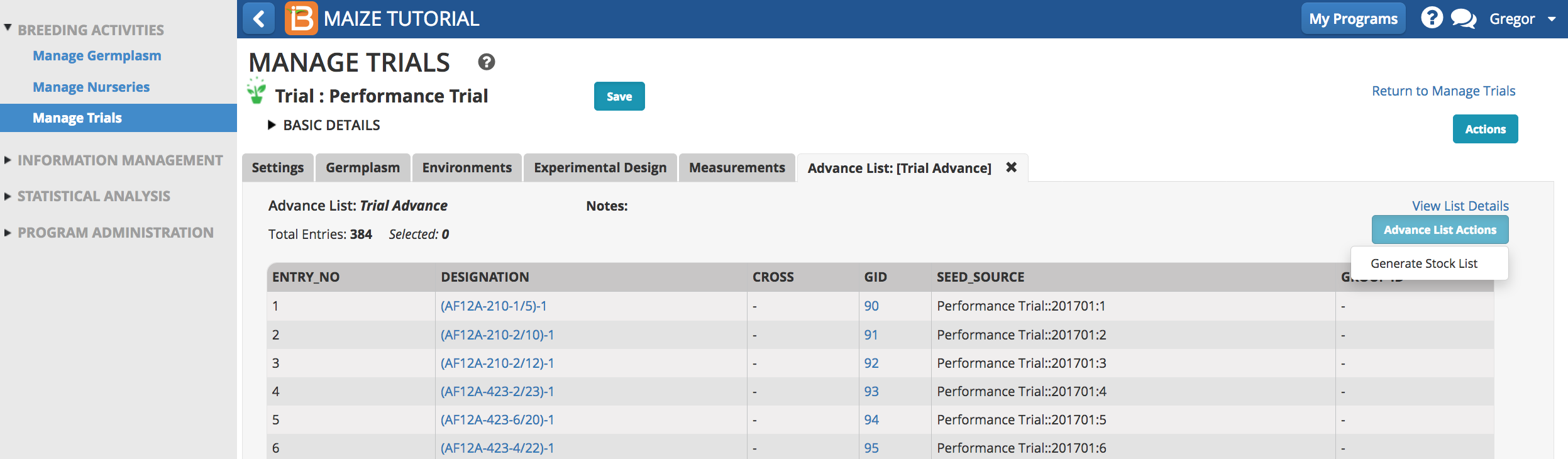
- Update inventory as described in Manage Nurseries.
Plant Level Sampling
The BMS supports plant level (within plot) sampling for genotypic data. See more in Manage Samples.