Genotypic Information
The parents used to develop this population were the synthetic wild allotetraploid [A. ipaënsis KG30076 (diploid BB genome) × A. duranensis V14167 (diploid AA genome)]4x used as the donor parent and the cultivated Fleur11 variety used as the recurrent parent. The final CSSL population is composed of 122 lines offering a wide coverage of the peanut genome with target wild chromosome segments of 39.2 cM on average. Most of the CSSLs (62 %) contain a single wild fragment in a homogeneous cultivated genetic background. A subset of 86 CSSLs has also been selected to provide a minimum set of lines with optimal genome coverage.
Dataset of genotypic data
The SSR genotyping data of the 122 lines are available for download from the Integrated Breeding Platform portal as part of the BMS Central Database for Groundnut.
Other Genotypic Resources
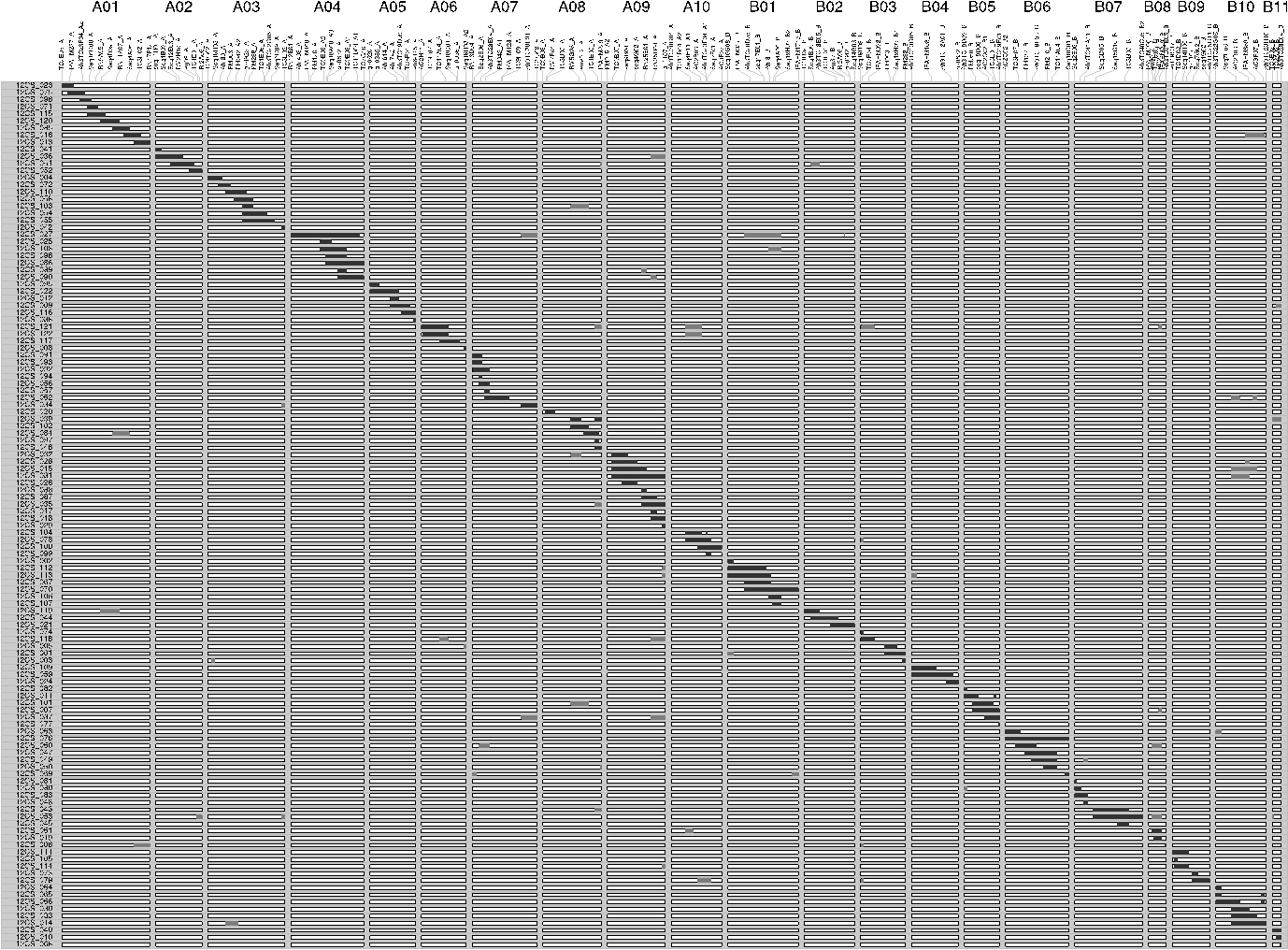
Detailed genotypic map of introgressions:- The following figure represents the graphical genotypes of the 122 lines. The 21 linkage groups of the map are named from A01 to A10 (A-genome) and from B01 to B11 (B-genome) and are represented vertically. The marker names are shown on each linkage group. The 122 CSSL are depicted horizontally. The black areas represent the wild target chromosome segments, while the white areas represent the Fleur11 genetic background, and the grey areas represent the wild supernumerary chromosome segments.
Phenotypic Information
Dataset of phenotypic data
A subset of 80 lines has been phenotyped along with the cultivated parent Fleur11 from September to December 2011 at the Centre National de Recherche Agronomique (CNRA) in Bambey (14.42uN and 16.28uW), Senegal. Four morphological traits have been recorded at 55–60 days after sowing:
- Flower color (YF) (orange versus yellow) visually rated visually.
- Peanut growth habit (GH) was measured as the ratio of the length of the creeping part of a given lateral branch to the total length of the lateral branch.
- Main stem height (PH) was measured from the cotyledonary axil to the terminal bud.
- Plant spread (PS) was measured as the distance between the widest branch tips.
Phenotyping data are available for download from the Integrated Breeding Platform portal as part of the BMS Central Database for Groundnut.
Supporting Information
- Fonceka, D., Hodo-Abalo, T., Rivallan, R., Faye, I., Sall, M.N., Ndoye, O., Favero, A., Bertioli, D., Glaszmann, J.-C., Courtois, B., et al. (2009). Genetic mapping of wild introgressions into cultivated peanut: a way toward enlarging the genetic basis of a recent allotetraploid, in BMC Plant Biol 9, 103.
- Fonceka, D., Tossim, H.-A., Rivallan, R., Vignes, H., Lacut, E., de Bellis, F., Faye, I., Ndoye, O., Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M., Valls, J.F.M., et al. (2012). Construction of Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Using a Wild Synthetic and QTL Mapping for Plant Morphology, in PLoS ONE 7, e48642.
- Fonceka, D., Tossim, H.-A., Rivallan, R., Vignes, H., Faye, I., Ndoye, O., Moretzsohn, M.C., Bertioli, D.J., Glaszmann, J.-C., Courtois, B., et al. (2012). Fostered and left behind alleles in peanut: interspecific QTL mapping reveals footprints of domestication and useful natural variation for breeding, in BMC Plant Biology 12, 26.
- Rami, J.-F., Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M., Foncéka, D., Moretzsohn, M.C., and Bertioli, D.J. (2014). Groundnut, in Alien Gene Transfer in Crop Plants, Volume 2, A. Pratap, and J. Kumar, eds. (Springer New York), pp. 253–279.