

Nuclear vs plastid inheritance (contd)
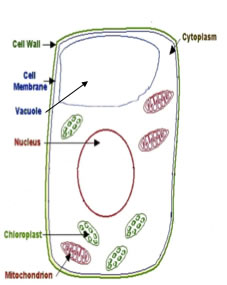 Some DNA is also present in the chloroplasts and the mitochondria. This is called plastid DNA and it includes a small number of genes.
Some DNA is also present in the chloroplasts and the mitochondria. This is called plastid DNA and it includes a small number of genes.
Because each leaf cell contains 20-100 chloroplasts and up to thousands of mitochrodria, the copy number of plastid genes per cell is large.
Plastids are rarely present in the pollen, and so are maternally inherited.
Unlike nuclear DNA, plastid DNA does not pass through meiosis, so is not affected by recombination.
Variation in plastid genes can arise by mutation.

