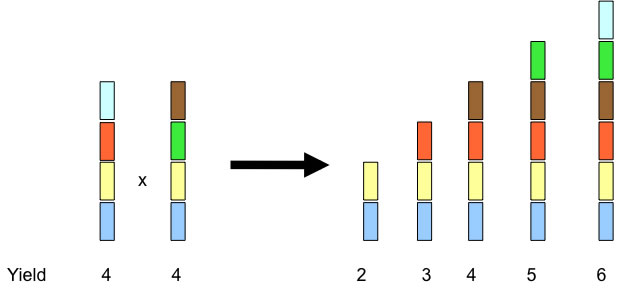
Additive genes
Additive genes are those which each contribute independently to a given trait.
These are the easiest for the breeder to handle.
For example suppose yield was determined by six genes, each of which had an equal effect on yield. If a cross is made between two varieties each with four "good" genes, then it should be possible to select plants with higher (or lower yield).